04 January 2021: Animal Study
Effect of Parecoxib Sodium on Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Rats
Fangyong Wu1AEG*, Wei Wang2ABD, Yingying Duan1BCF, Jia Guo1CD, Guanhua Li2BF, Tao Ma2DFDOI: 10.12659/MSM.928205
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e928205
Abstract
BACKGROUND: We aimed to explore the effect of parecoxib sodium on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury rats and its mechanism.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: The coronary artery of Sprague-Dawley rats was occluded for 6 h of myocardial ischemia, followed by reperfusion for 30 min (I/R group). Before ischemia, parecoxib sodium (10 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected twice a day for 3 consecutive days, followed by reperfusion for 6 h (I/R+Pare group). The cardiac function and changes in the infarction area were evaluated via echocardiography in each group. The differences in the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins were determined via immunohistochemistry and western blotting. Then, the percentage of reactive oxygen species (ROS)⁺ cells and the content of lipid peroxide were detected, based on which the degree of oxidative stress was evaluated. Next, the expressions of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf-2) signaling pathways and downstream target genes were determined using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
RESULTS: After treatment with parecoxib sodium, the cardiac function of I/R injury rats was restored, and the infarction area and apoptosis level were reduced (P<0.05). Parecoxib sodium reduced the levels of ROS and lipid peroxidation in myocardial I/R injury rats, thereby weakening oxidative stress. It also regulated the redox imbalance caused by I/R injury through regulating NF-κB and Nrf-2 (P<0.01). In addition, after treatment with parecoxib sodium, NF-κB was significantly downregulated, while Nrf-2 was upregulated, and the content of proinflammatory cytokines was obviously reduced (P<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS: Parecoxib sodium exerts a protective effect against myocardial I/R injury through regulating antioxidant and inflammatory mechanisms.
Keywords: NF-E2-Related Factor 2, Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappa B, Cardiotonic Agents, Cytokines, Heart Function Tests, Inflammation Mediators, Isoxazoles, Myocardial Reperfusion Injury, Myocardium
Background
Ischemia is caused by insufficient oxygen supply in tissues, and long-term ischemia and subsequent reperfusion will lead to severe irreversible myocardial injury [1,2]. The clinical treatment methods of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury include thrombolysis, heart transplantation, and coronary artery bypass grafting [3,4]. Due to the diverse consequences of reperfusion injury, including the increase in production of oxygen free radicals and Ca2+ level, loss of membrane phospholipids, and endothelial dysfunction [5,6], the myocardial function is altered.
I/R injury is the result of complex interactions among various inflammatory mediators, in which the inflammatory factor cyclooxygenase (COX) and its derived prostaglandin play a key role [7,8]. COX has 2 isoenzymes (COX-1 and COX-2). COX-2 is expressed at very low levels under normal conditions, but it can be rapidly expressed under pathological conditions, especially in the immune system [9,10]. According to previous studies, both COX-1 and COX-2 are involved in skeletal muscle and gastric I/R injury [11,12]. Knockout of COX-2 can significantly reduce I/R-induced liver injury [9]. However, the mechanism of COX-2 in myocardial I/R injury remains unclear. In this study, the protective mechanism of COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib sodium against myocardial I/R injury was explored, so as to provide a clinical therapeutic strategy for myocardial I/R injury.
Material and Methods
LABORATORY MATERIALS:
We used parecoxib sodium (Pfizer, New York, NY, USA), SYBR Green quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) Master Mix (2×) (Fermentas, Waltham, MA, USA), TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA).
STUDY ANIMALS:
Sixty Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into a Sham group (n=20) [suture around the left anterior descending artery (LAD) only, without ligation], an I/R group (n=20), and an I/R+Pare group (n=20, intraperitoneal injection of parecoxib sodium before ischemia). This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Eastern Medical District of the Chinese PLA General Hospital Animal Center.
ESTABLISHMENT OF A LABORATORY ANIMAL MODEL OF I/R:
On the 4th day after adaptation to the environment, the operation was performed. After drug-induced anesthesia, the trachea was cut open and intubated, and the limbs were connected to an electrocardiograph. A horizontal incision was made in the muscle between the fourth and fifth ribs, and the chest was opened. Then, the LAD was ligated with a 6-0 silk suture, and a silicon tube (outer diameter: 1 mm) was placed above the LAD for ischemia. The success of I/R injury was determined based on the changes in electrocardiogram (arched ST segment elevation of Q lead or high-amplitude T-wave for 0.1 mV). The silicone tube was removed after 30 min to restore the normal circulation for 4 h. In the Sham group, the rats were only sutured around the LAD, without ligation.
DRUG PREPARATION AND TIMEPOINTS OF ADMINISTRATION:
Parecoxib sodium was diluted in isotonic saline. In the I/R+Pare group, before ischemia, parecoxib sodium (10 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected twice a day for 3 consecutive days. In the Sham group and I/R group, an equal volume of isotonic saline was intraperitoneally injected at the same timepoints.
DETERMINATION OF GENE EXPRESSION IN MYOCARDIAL TISSUES AND SERUM:
The total RNA was isolated from myocardial tissues using TRIzol reagent, and reverse-transcribed into complementary deoxyribose nucleic acid (cDNA), followed by real-time qPCR. The gene expression was standardized with β-actin, with the genes in the Sham group were used as references. Then, the levels of serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were measured using ELISA kits. The primer sequences were as follows:
EVALUATION OF LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION:
Left ventricular function was evaluated using transthoracic echocardiography. Under anesthesia, the chest hair was shaved off, and left ventricular electrocardiography was performed. The left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP), maximal rate of the increase/decrease of left ventricular pressure (±dp/dtmax), and left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) were assessed and recorded in at least 3 cardiac cycles, and the averages were taken.
EVALUATION OF MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AREA:
The myocardial tissues were cut into sections and incubated with 1% 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) for 15 min to identify the infarction region (red: non-infarction region, white: infarction region). The infarction area was analyzed using software, and the average was taken. Weight of infarction region=percentage of infarction area in each part×weight of the part.
DETECTION OF REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES (ROS) AND LIPID PEROXIDE MALONDIALDEHYDE (MDA) IN MYOCARDIAL TISSUES:
The tissue samples were incubated in 50 μL of 30 μM H2DCFDA stock solution for 30 min, and the mixture was centrifuged. Then, the fluorescence intensity was detected using the 485/520 nm filter set, indicating the percentage of ROS content.
The absorbance of myocardial tissue samples was measured at 532 nm via thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) assay, indicating the MDA protein (mg) required for the formation of 1 nmoL TBARS.
WESTERN BLOT ANALYSIS:
The myocardial tissues were collected in each group and ground with lysis buffer in a homogenizer, and the protein concentration was measured. The target protein was separated via electrophoresis, transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA), and incubated with the primary antibody overnight and then with secondary antibody, followed by image development. Finally, the gray value of bands was analyzed.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS:
The experimental data were statistically analyzed using Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) 17.0 software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Comparison between multiple groups was done using one-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc test (least significant difference).
Results
EFFECT OF PARECOXIB SODIUM ON CARDIAC FUNCTION OF RATS:
The changes in cardiac function were reflected by LVSP (mmHg), ±dp/dtmax (mmHg/s) and LVEDP (mmHg), and the severity of I/R injury was evaluated via the infarction area. We found that after coronary occlusion, LVSP, ±dp/dtmax and LVEDP significantly declined, and the infarction area became larger (P<0.05). After treatment with parecoxib sodium, LVSP, ±dp/dtmax and LVEDP were significantly restored, and the infarction area was not increased (Figure 1). These results show that parecoxib sodium restores the cardiac systolic/diastolic function and inhibits the increase in infarction area in myocardial I/R injury rats.
PARECOXIB SODIUM REDUCED I/R-INDUCED MYOCARDIAL APOPTOSIS:
There is increasing evidence that the number of apoptotic cells increases in I/R rats. Therefore, the changes in the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins were detected to study the effect of parecoxib sodium on myocardial apoptosis during myocardial I/R. In the I/R group, the expression of Bcl-2 declined, while that of Bax obviously rose in myocardial tissues, similar to the results of western blot analysis. These findings suggest that myocardial apoptosis is accelerated during myocardial I/R. After treatment with parecoxib sodium, the expressions of apoptosis-related genes in myocardial tissues showed the opposite trends (P<0.05) (Figure 2). These results show that parecoxib sodium is helpful for inhibiting myocardial apoptosis.
PARECOXIB SODIUM RELIEVED OXIDATIVE STRESS INDUCED BY MYOCARDIAL I/R INJURY:
Research indicates that myocardial I/R injury can cause oxidative stress. Therefore, the effect of parecoxib sodium on ROS was explored after I/R injury. Our results showed that the production of ROS was greatly accelerated by I/R injury (P<0.05), while it was evidently reduced in myocardial tissues after treatment with parecoxib sodium (P<0.05). Similarly, the level of the end-product of lipid peroxidation, MDA, was also increased after I/R, while it was reduced after treatment with parecoxib sodium (P<0.05) (Figure 3). The above results suggest that parecoxib sodium can effectively relieve the oxidative stress induced by myocardial I/R injury.
PARECOXIB SODIUM REDUCED CONTENT OF INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES AFTER MYOCARDIAL I/R INJURY:
Myocardial I/R leads to increased expressions of inflammatory factors and neutrophil infiltration, so anti-inflammatory drugs can markedly improve I/R injury treatment efficacy. The changes in gene expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 in myocardial tissues were determined via qPCR, so as to reflect the inflammatory response in each group. As shown in Figure 4, the mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 in myocardial tissues were increased by 15 and 17 times, respectively, in the I/R group compared with those in the Sham group. After treatment with parecoxib sodium, their mRNA expressions were decreased by 40% and 63%, respectively. The expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 in serum were similar to those in myocardial tissues (P<0.05). These findings suggest that parecoxib sodium has an anti-inflammatory effect in myocardial tissues, which can inhibit the expressions of inflammatory factors.
PARECOXIB SODIUM EXERTED A CARDIOPROTECTIVE EFFECT IN MYOCARDIAL I/R INJURY RATS VIA ACTIVATING NRF-2:
Compared with those in the Sham group, NF-κB was upregulated (P<0.05) and Nrf-2 and its target genes were downregulated in the I/R group, thus leading to oxidative stress and inflammation. After treatment with parecoxib sodium, Nrf-2 was activated, and the mRNA expressions of HO-1 and GST were also increased (P<0.05). Compared with those in the I/R group, the mRNA expressions of inflammatory markers NF-κB, COX-2 and iNOS were lower in the I/R+Pare group (P<0.05) (Figure 5).
Discussion
A recent study showed that parecoxib results in renal protection in an induced-ischemia rat model [13]. In the present study, it was confirmed that parecoxib sodium had an obvious protective effect against I/R injury, and it regulated oxidative stress and inflammation through the Nrf-2 and NF-κB pathways. In other words, parecoxib sodium can effectively prevent myocardial I/R injury through upregulating Nrf-2 expression and downregulating NF-κB expression.
Myocardial I/R injury damages the myocardial blood supply, causing irreversible cardiac damage, ultimately leading to myocardial apoptosis and necrosis and facilitating myocardial infarction [14,15]. During reperfusion, ischemic myocardia absorb the molecular oxygen again, and the number of ROS also increases [16,17]. Antioxidants can regulate the occurrence and development of myocardial I/R injury, thereby exerting a therapeutic effect. In the present study, the effect of parecoxib sodium on cardiac function was first evaluated through cardiac systolic/diastolic indexes. We found that parecoxib sodium partially restored cardiac function and inhibited the increase of infarction area in I/R injury rats, indicating that parecoxib sodium can alleviate I/R injury in rats. Furthermore, parecoxib sodium effectively prevented myocardial oxidative stress through reducing the levels of ROS and lipid peroxide, thereby suppressing myocardial apoptosis. In addition, parecoxib sodium reduced the levels of inflammatory factors in myocardial tissues and serum in I/R injury rats, thus exerting an anti-inflammatory effect. To sum up, as an antioxidant, parecoxib sodium can relieve cardiac dysfunction caused by myocardial I/R injury.
The main mechanism of regulating oxidative stress and inflammation is to restore the redox balance in cells [18]. With the help of antioxidants, excess free radicals can be eliminated in cells to keep the redox balance, thereby preventing activation of inflammatory mediators. Under redox imbalance, NF-κB is activated, and COX-2 gene expression is regulated [19,20]. In this study, it was found that the expressions of NF-κB and its downstream targets COX-2 and iNOS were activated by myocardial I/R injury. The oxidative stress level and expressions of inflammatory proteins were reduced after treatment with parecoxib sodium. Moreover, the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 were decreased in myocardial tissues and serum in the I/R+Pare group compared with those in the I/R group, confirming the anti-inflammatory effect of parecoxib sodium. Our results show that parecoxib sodium can regulate the expressions of NF-κB and its downstream targets COX-2 and iNOS through regulating the ROS level.
Nrf-2 is a transcription factor sensitive to the body’s redox reaction, which can regulate the redox state in cells. Nrf-2 monitors the oxidation state in cells at the basal level, prevents cellular oxidation, and keeps a basic antioxidant state. In the case of destruction of Nrf-2, excessive oxidative stress and inflammation will be caused, resulting in various diseases [21–23]. In the present study, oxidative stress and inflammation were enhanced by myocardial I/R injury, which may be related to the downregulation of Nrf-2 level and antioxidant enzyme activity. In addition, the expressions of Nrf-2 and its downstream targets GST and HO-1 were remarkably upregulated in the I/R+Pare group compared with those in the I/R group. The above findings demonstrate that parecoxib sodium relieves oxidative stress and inflammation in I/R injury rats by raising Nrf-2 expression and improving the antioxidant state.
Conclusions
In conclusion, parecoxib sodium regulates myocardial oxidative stress and inflammatory response via regulating Nrf-2 expression, thereby exerting a protective effect against myocardial I/R injury.
Figures
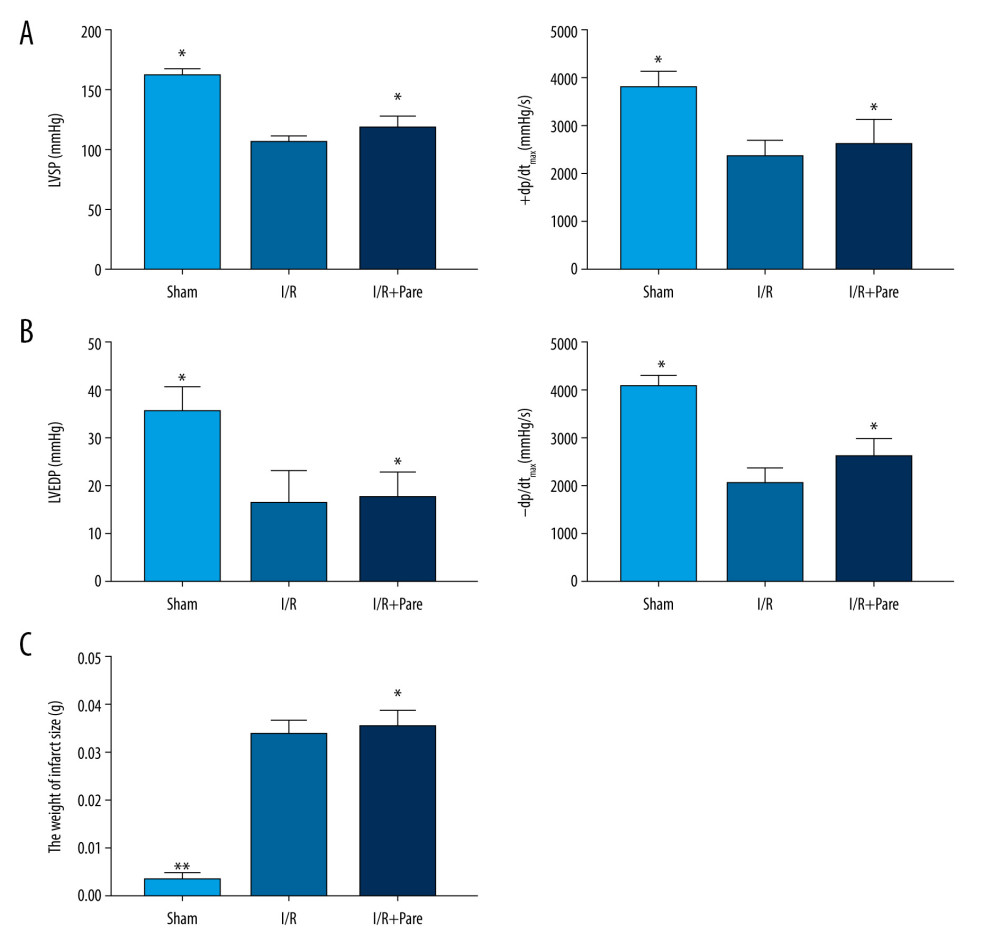 Figure 1. Effect of parecoxib sodium on cardiac function of rats. (A) Changes in left ventricular systolic function of rats. LVSP and +dp/dtmax were remarkably higher in the Sham group than those in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (B) Changes in left ventricular diastolic function of rats. LVEDP and −dp/dtmax were remarkably higher in the Sham group than those in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (C) Changes in weight of myocardial infarction region. The infarction area was remarkably smaller in the Sham group than that in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group)
Figure 1. Effect of parecoxib sodium on cardiac function of rats. (A) Changes in left ventricular systolic function of rats. LVSP and +dp/dtmax were remarkably higher in the Sham group than those in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (B) Changes in left ventricular diastolic function of rats. LVEDP and −dp/dtmax were remarkably higher in the Sham group than those in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (C) Changes in weight of myocardial infarction region. The infarction area was remarkably smaller in the Sham group than that in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group) 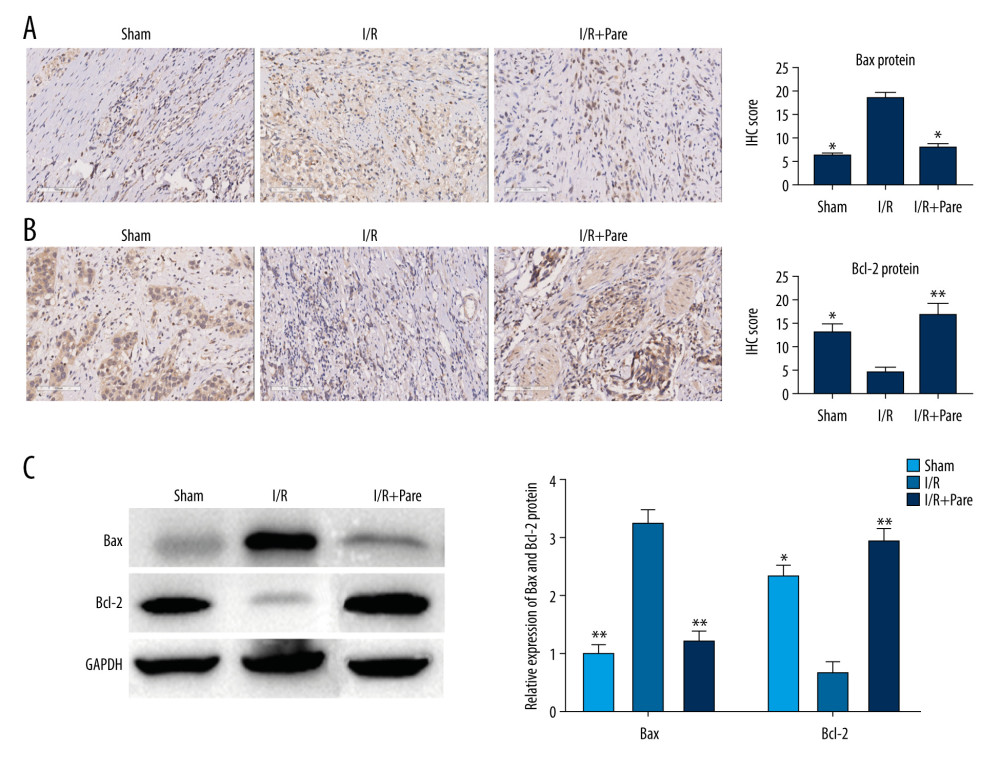 Figure 2. Effect of parecoxib sodium on the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in myocardial tissues. (A, B) Changes in Bcl-2 and Bax expressions in myocardial tissues detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC). The Sham group and I/R+Pare group had higher IHC scores of Bcl-2 and lower IHC scores of Bax than in the I/R group (P<0.05) (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group). (C) Changes in Bcl-2 and Bax expressions in myocardial tissues detected using western blotting. The Sham group and I/R+Pare group had an obviously higher protein expression of Bcl-2 and a lower protein expression of Bax than in the I/R group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group).
Figure 2. Effect of parecoxib sodium on the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in myocardial tissues. (A, B) Changes in Bcl-2 and Bax expressions in myocardial tissues detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC). The Sham group and I/R+Pare group had higher IHC scores of Bcl-2 and lower IHC scores of Bax than in the I/R group (P<0.05) (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group). (C) Changes in Bcl-2 and Bax expressions in myocardial tissues detected using western blotting. The Sham group and I/R+Pare group had an obviously higher protein expression of Bcl-2 and a lower protein expression of Bax than in the I/R group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group). 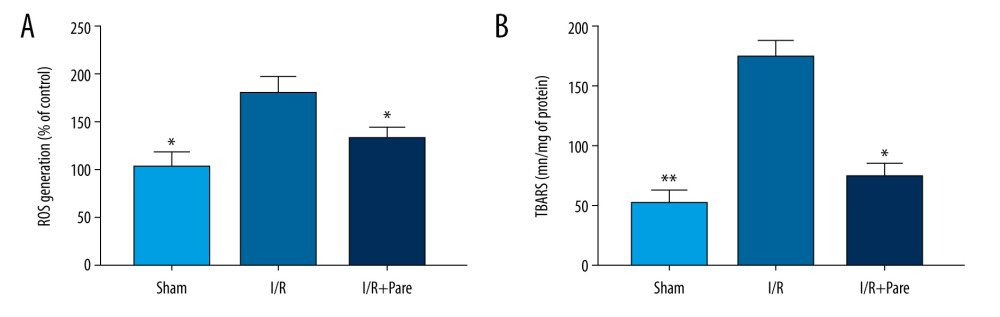 Figure 3. Parecoxib sodium relieved oxidative stress induced by myocardial I/R injury. (A) Percentage of ROS+ cells in myocardial tissues. The proportion of ROS+ cells was higher in the I/R group than that in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (B) Difference in MDA protein concentration in myocardial tissues. Compared with that in the I/R group, MDA protein concentration were clearly lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.01). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group).
Figure 3. Parecoxib sodium relieved oxidative stress induced by myocardial I/R injury. (A) Percentage of ROS+ cells in myocardial tissues. The proportion of ROS+ cells was higher in the I/R group than that in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (B) Difference in MDA protein concentration in myocardial tissues. Compared with that in the I/R group, MDA protein concentration were clearly lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.01). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group). 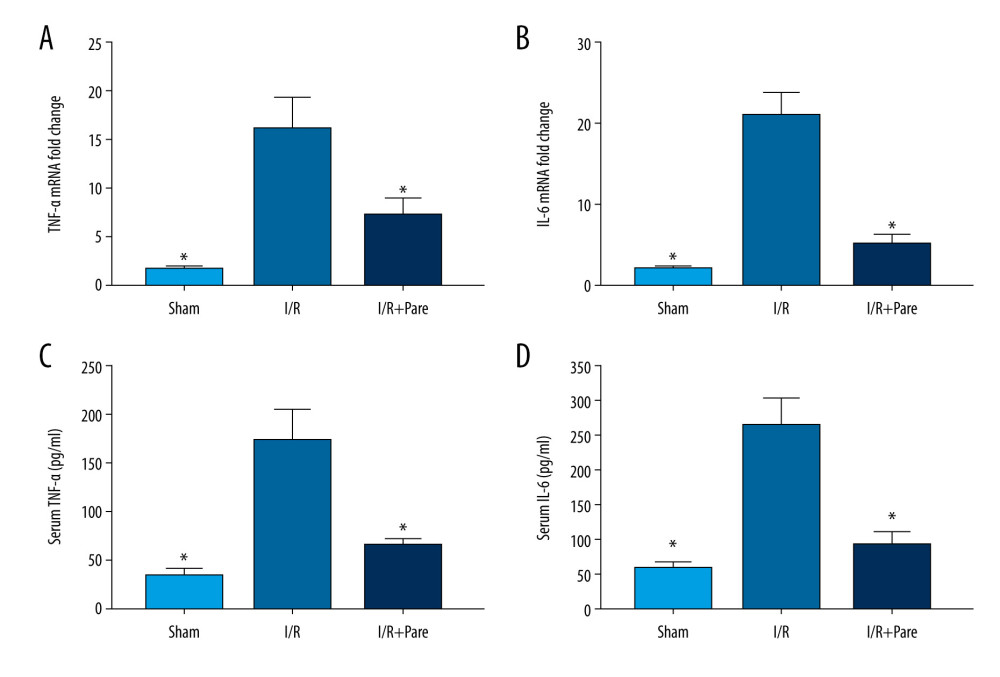 Figure 4. Effects of parecoxib sodium on expressions of myocardial I/R proinflammatory cytokines. (A, B) Differences in mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 in myocardial tissues. The relative mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 were markedly lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group than those in the I/R group (P<0.05). (C, D) Expressions of serum TNF-α and IL-6 in each group. The expressions of serum TNF-α and IL-6 were lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group than those in the I/R group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group).
Figure 4. Effects of parecoxib sodium on expressions of myocardial I/R proinflammatory cytokines. (A, B) Differences in mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 in myocardial tissues. The relative mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 were markedly lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group than those in the I/R group (P<0.05). (C, D) Expressions of serum TNF-α and IL-6 in each group. The expressions of serum TNF-α and IL-6 were lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group than those in the I/R group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group). 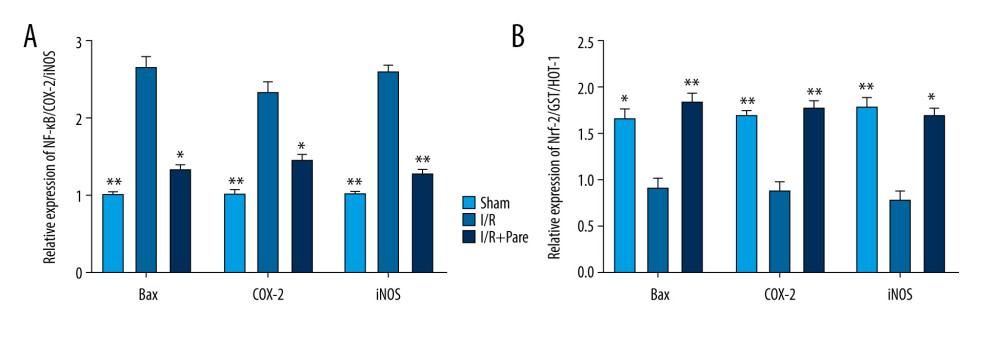 Figure 5. Effects of parecoxib sodium on activity of NF-κB and Nrf-2 signaling pathways. (A, B) Relative expressions of NF-κB and Nrf-2 pathways and target genes detected via PCR. The relative expressions of NF-κB pathway and its target genes were higher in the I/R group than those in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). The relative expressions of Nrf-2 pathway and its target genes were lower in the I/R group than those in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.01). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group).
Figure 5. Effects of parecoxib sodium on activity of NF-κB and Nrf-2 signaling pathways. (A, B) Relative expressions of NF-κB and Nrf-2 pathways and target genes detected via PCR. The relative expressions of NF-κB pathway and its target genes were higher in the I/R group than those in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). The relative expressions of Nrf-2 pathway and its target genes were lower in the I/R group than those in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.01). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group). References
1. Paradies G, Paradies V, Ruggiero FM, Petrosillo G, Mitochondrial bioenergetics and cardiolipin alterations in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: Implications for pharmacological cardioprotection: Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2018; 315(5); H1341-52
2. Lesnefsky EJ, Chen Q, Tandler B, Hoppel CL, Mitochondrial dysfunction and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion: Implications for novel therapies: Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 2017; 57; 535-65
3. Moskowitzova K, Shin B, Liu K, Mitochondrial transplantation prolongs cold ischemia time in murine heart transplantation: J Heart Lung Transplant, 2019; 38(1); 92-99
4. Saclı H, Kara I, Diler MS, The relationship between the use of cold and isothermic blood cardioplegia solution for myocardial protection during cardiopulmonary bypass and the ischemia-reperfusion injury: Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2019; 25(6); 296-303
5. Münzel T, Daiber A, Inorganic nitrite and nitrate in cardiovascular therapy: A better alternative to organic nitrates as nitric oxide donors?: Vascul Pharmacol, 2018; 102; 1-10
6. Ishiwata-Endo H, Kato J, Role of a TRIM72 ADP-ribosylation cycle in myocardial injury and membrane repair: JCI Insight, 2018; 3(22); e97898
7. Stankowska DL, Nam MH, Nahomi RB, Systemically administered peptain-1 inhibits retinal ganglion cell death in animal models: implications for neuroprotection in glaucoma: Cell Death Discov, 2019; 5; 112
8. Zhu L, Xu C, Huo X, The cyclooxygenase-1/mPGES-1/endothelial prostaglandin EP4 receptor pathway constrains myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: Nat Commun, 2019; 10(1); 1888
9. Hunter D, Chai C, Barr GA, Effects of COX inhibition and LPS on formalin induced pain in the infant rat: Dev Neurobiol, 2015; 75(10); 1068-79
10. Wójcik P, Biernacki M, Wroński A, Altered lipid metabolism in blood mononuclear cells of psoriatic patients indicates differential changes in psoriasis vulgaris and psoriatic arthritis: Int J Mol Sci, 2019; 20(17); 4249
11. Lavin KM, Perkins RK, Jemiolo B, Effects of aging and lifelong aerobic exercise on basal and exercise-induced inflammation: J Appl Physiol (1985), 2020; 128(1); 87-99
12. Tiwari SK, Shaik AS, Shaik AP, Gene expression patterns of COX-1, COX-2 and iNOS in H. Pylori infected histopathological conditions: Microb Pathog, 2019; 135; 103634
13. Calistro Neto JP, da Torres RC, Gonçalves GM, Parecoxib reduces renal injury in an ischemia/reperfusion model in rats: Acta Cir Bras, 2015; 30(4); 270-76
14. Sun T, Cheng YT, Yan LX, LncRNA MALAT1 knockdown alleviates myocardial apoptosis in rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion through activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway: Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019; 23(23); 10523-31
15. Wu T, Jiang N, Ji Z, Shi G, The IRE1 signaling pathway is involved in the protective effect of low-dose LPS on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: Life Sci, 2019; 231; 116569
16. Zhao J, Jie Q, Li G, Rac1 promotes the survival of H9c2 cells during serum deficiency targeting JNK/c-JUN/Cyclin-D1 and AKT2/MCL1 pathways: Int J Med Sci, 2018; 15(10); 1062-71
17. Wu L, Tan JL, Chen ZY, Huang G, Cardioprotection of post-ischemic moderate ROS against ischemia/reperfusion via STAT3-induced the inhibition of MCU opening: Basic Res Cardiol, 2019; 114(5); 39
18. Mantzarlis K, Tsolaki V, Zakynthinos E, Role of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis and potential therapies: Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2017; 2017 5985209
19. Wang SX, Wang J, Shao JB, Plumbagin mediates cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through Nrf-2 signaling: Med Sci Monit, 2016; 22; 1250-57
20. Qi G, Mi Y, Fan R, Nobiletin protects against systemic inflammation-stimulated memory impairment via MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways: J Agric Food Chem, 2019; 67(18); 5122-34
21. Li H, Shi Y, Wang X, Piceatannol alleviates inflammation and oxidative stress via modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB pathways in diabetic cardiomyopathy: Chem Biol Interact, 2019; 310; 108754
22. Mahmoud AR, Ali FEM, Abd-Elhamid TH, Hassanein EHM, Coenzyme Q10 protects hepatocytes from ischemia reperfusion-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress via regulation of Bax/Bcl-2/PUMA and Nrf-2/FOXO-3/Sirt-1 signaling pathways: Tissue Cell, 2019; 60; 1-13
23. Khurana N, Sikka SC, Targeting crosstalk between Nrf-2, NF-κB and androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer: Cancers (Basel), 2018; 10(10); 352
Figures
 Figure 1. Effect of parecoxib sodium on cardiac function of rats. (A) Changes in left ventricular systolic function of rats. LVSP and +dp/dtmax were remarkably higher in the Sham group than those in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (B) Changes in left ventricular diastolic function of rats. LVEDP and −dp/dtmax were remarkably higher in the Sham group than those in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (C) Changes in weight of myocardial infarction region. The infarction area was remarkably smaller in the Sham group than that in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group)
Figure 1. Effect of parecoxib sodium on cardiac function of rats. (A) Changes in left ventricular systolic function of rats. LVSP and +dp/dtmax were remarkably higher in the Sham group than those in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (B) Changes in left ventricular diastolic function of rats. LVEDP and −dp/dtmax were remarkably higher in the Sham group than those in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (C) Changes in weight of myocardial infarction region. The infarction area was remarkably smaller in the Sham group than that in the I/R group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group) Figure 2. Effect of parecoxib sodium on the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in myocardial tissues. (A, B) Changes in Bcl-2 and Bax expressions in myocardial tissues detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC). The Sham group and I/R+Pare group had higher IHC scores of Bcl-2 and lower IHC scores of Bax than in the I/R group (P<0.05) (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group). (C) Changes in Bcl-2 and Bax expressions in myocardial tissues detected using western blotting. The Sham group and I/R+Pare group had an obviously higher protein expression of Bcl-2 and a lower protein expression of Bax than in the I/R group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group).
Figure 2. Effect of parecoxib sodium on the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in myocardial tissues. (A, B) Changes in Bcl-2 and Bax expressions in myocardial tissues detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC). The Sham group and I/R+Pare group had higher IHC scores of Bcl-2 and lower IHC scores of Bax than in the I/R group (P<0.05) (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group). (C) Changes in Bcl-2 and Bax expressions in myocardial tissues detected using western blotting. The Sham group and I/R+Pare group had an obviously higher protein expression of Bcl-2 and a lower protein expression of Bax than in the I/R group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group). Figure 3. Parecoxib sodium relieved oxidative stress induced by myocardial I/R injury. (A) Percentage of ROS+ cells in myocardial tissues. The proportion of ROS+ cells was higher in the I/R group than that in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (B) Difference in MDA protein concentration in myocardial tissues. Compared with that in the I/R group, MDA protein concentration were clearly lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.01). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group).
Figure 3. Parecoxib sodium relieved oxidative stress induced by myocardial I/R injury. (A) Percentage of ROS+ cells in myocardial tissues. The proportion of ROS+ cells was higher in the I/R group than that in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). (B) Difference in MDA protein concentration in myocardial tissues. Compared with that in the I/R group, MDA protein concentration were clearly lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.01). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group). Figure 4. Effects of parecoxib sodium on expressions of myocardial I/R proinflammatory cytokines. (A, B) Differences in mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 in myocardial tissues. The relative mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 were markedly lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group than those in the I/R group (P<0.05). (C, D) Expressions of serum TNF-α and IL-6 in each group. The expressions of serum TNF-α and IL-6 were lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group than those in the I/R group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group).
Figure 4. Effects of parecoxib sodium on expressions of myocardial I/R proinflammatory cytokines. (A, B) Differences in mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 in myocardial tissues. The relative mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 were markedly lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group than those in the I/R group (P<0.05). (C, D) Expressions of serum TNF-α and IL-6 in each group. The expressions of serum TNF-α and IL-6 were lower in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group than those in the I/R group (P<0.05). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group). Figure 5. Effects of parecoxib sodium on activity of NF-κB and Nrf-2 signaling pathways. (A, B) Relative expressions of NF-κB and Nrf-2 pathways and target genes detected via PCR. The relative expressions of NF-κB pathway and its target genes were higher in the I/R group than those in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). The relative expressions of Nrf-2 pathway and its target genes were lower in the I/R group than those in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.01). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group).
Figure 5. Effects of parecoxib sodium on activity of NF-κB and Nrf-2 signaling pathways. (A, B) Relative expressions of NF-κB and Nrf-2 pathways and target genes detected via PCR. The relative expressions of NF-κB pathway and its target genes were higher in the I/R group than those in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.05). The relative expressions of Nrf-2 pathway and its target genes were lower in the I/R group than those in the Sham group and I/R+Pare group (P<0.01). (* P<0.05 vs. I/R group, ** P<0.01 vs. I/R group). In Press
07 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Knowledge of and Attitudes Toward Clinical Trials: A Questionnaire-Based Study of 179 Male Third- and Fourt...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943468
08 Mar 2024 : Animal Research
Modification of Experimental Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) in Rat Pups by Single Exposure to Hyp...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943443
18 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Comparative Analysis of Open and Closed Sphincterotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Anal Fissure: Safety an...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.944127
08 Mar 2024 : Laboratory Research
Evaluation of Retentive Strength of 50 Endodontically-Treated Single-Rooted Mandibular Second Premolars Res...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.944110
Most Viewed Current Articles
17 Jan 2024 : Review article
Vaccination Guidelines for Pregnant Women: Addressing COVID-19 and the Omicron VariantDOI :10.12659/MSM.942799
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942799
14 Dec 2022 : Clinical Research
Prevalence and Variability of Allergen-Specific Immunoglobulin E in Patients with Elevated Tryptase LevelsDOI :10.12659/MSM.937990
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e937990
16 May 2023 : Clinical Research
Electrophysiological Testing for an Auditory Processing Disorder and Reading Performance in 54 School Stude...DOI :10.12659/MSM.940387
Med Sci Monit 2023; 29:e940387
01 Jan 2022 : Editorial
Editorial: Current Status of Oral Antiviral Drug Treatments for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Non-Hospitalized Pa...DOI :10.12659/MSM.935952
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e935952








