15 March 2021: Lab/In Vitro Research
Long Noncoding RNA TCONS_00068220 Promotes Breast Cancer Progression by Regulating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Marker E-Cadherin
Xiao Liu12ABEF, Xingsong Tian1ACDG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.929832
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e929832
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play essential roles in the regulation of breast cancer development. We herein investigated the potential role of lncRNA TCONS_00068220 in breast cancer pathogenesis.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: The expression levels of TCONS_00068220 in breast cancer tissues were measured by qRT-PCR. Afterwards, TCONS_00068220 was (1) overexpressed in MCF-7 breast cancer cells, and (2) silenced in MDA-MB-231 cells. Then, CCK-8 and transwell assays were conducted to detect the impact of TCONS_00068220 on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. The expression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) marker E-cadherin was detected by western blot assay after upregulation or downregulation of TCONS_00068220.
RESULTS: TCONS_00068220 was remarkably upregulated in breast cancer tissues compared with non-cancerous tissues. In addition, TCONS_00068220 level was significantly correlated with lymphatic metastasis, Ki67 index, clinical stage, and differentiation grade. All breast cancer cell lines displayed a higher expression level of TCONS_00068220 compared with the normal breast epithelial cell line MCF-10A. Furthermore, enhanced expression of TCONS_00068220 in MCF-7 cells promoted cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT, whereas TCONS_00068220 knockdown in MDA-MB-231 cells led to the opposite results. E-cadherin was negatively regulated by TCONS_00068220 in both breast cancer tissues and cell lines. Finally, TCONS_00068220 regulated MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cell behaviors by downregulating E-cadherin.
CONCLUSIONS: TCONS_00068220 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, while facilitating the process of EMT by interacting with E-cadherin and suppressing its expression. Therefore, it may potentially serve as an oncogene in breast cancer progression.
Keywords: Breast Neoplasms, Antigens, CD, Breast, Cadherins, MCF-7 cells
Background
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous and complex neoplasm that represents one of the most common malignancies diagnosed in females worldwide [1]. Breast cancer is a lethal disease characterized by high mortality and poor prognosis [2,3]. It has been reported that approximately 25–40% of breast cancer patients display drug resistance, recurrence, or distant metastasis within 5 years [4], despite the greatly improved outcomes offered by surgery and targeted therapies [5]. Therefore, a better understanding of breast cancer pathogenesis and identification of molecular therapeutic targets is needed.
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a class of endogenous, regulatory RNA molecules that are longer than 200 nucleotides. They regulate gene expression in most cases by altering the activity of the upstream promoter region [6]. It has been shown that lncRNAs are dysregulated in diverse pathological processes underlying the development of different human diseases [7,8]. Increasing evidence is revealing that various lncRNAs play vital roles in oncogenesis, and their aberrant expression is involved in tumor growth, metastasis, and other aggressive behaviors [9–14]. For example, lncRNA H19 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, clone formation, and cancer stem cell generation [11]. The expression of OIP5-AS1 is considerably elevated in breast cancer, and OIP5-AS1 knockdown impairs the malignant phenotype of breast cancer cells [12]. Another well-known lncRNA, HOTAIR, is also upregulated in breast cancer, and has been demonstrated to facilitate tumor metastasis [13]. Moreover, PANDAR modulates G1/S arrest in breast cancer cells by targeting the downstream gene INK4A [14].
The novel lncRNA TCONS_00068220 is a 1281-nucleotide-long transcript originating from the human chromosome 8q11.21. It is highly abundant in digestive organs and glands. Nevertheless, neither the effect of expression alterations of TCONS_00068220 nor its potential role, if any, in the pathogenesis of carcinomas has been reported, with the rare exceptions of previous studies suggesting that TCONS_00068220 was overexpressed in gastric cancer samples and that silencing its expression contributed to enhanced cell apoptosis [15,16].
Herein, we found that the level of TCONS_00068220 was significantly upregulated in breast cancer patients, suggesting an oncogenic role of TCONS_00068220 in breast tumor development. Additionally, further investigation showed that the abnormal expression of TCONS_00068220 was related to changes in the phenotypes of breast cancer cells, including proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), migration, and invasion. These findings provide new insight that could lead to new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for breast cancer.
Material and Methods
PATIENTS AND TISSUE SAMPLES:
Paired breast cancer tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues were collected from 60 female patients diagnosed with triple-negative breast-infiltrating ductal carcinoma from Jan 2015 to July 2018. Patients were excluded from this study if they received radiotherapy or chemotherapy treatment before surgery. Informed consent was provided by each patient prior to surgery. All procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of Chinese Medicine Hospital of Tai’an City (Tai’an, Shandong, China).
CELL CULTURE:
Human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, and normal breast epithelial cell line MCF-10A were obtained from ATCC (Manassas, Virginia, USA). Breast cancer cell lines were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM, Gibco, Rockville, MD, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, Rockville, MD, USA), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 mg/mL streptomycin. The MCF10A cells were cultured in a DMEM/F12 medium containing EGF (20 ng/mL), hydrocortisone (0.5 mg/mL), and cholera toxin (100 ng/mL) (Sigma-Aldrich; St. Louis, MO, USA), with insulin (10 μg/mL), and 1× penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco; Carlsbad, CA, USA). Cells were stored at 37°C in 5% CO2.
PLASMID TRANSFECTION:
Full-length lncRNA TCONS_00068220 (XR_928848.2) was cloned into pLVX-Puro to construct a recombinant plasmid, which was referred to as pLVX-TCONS_00068220. The empty pLVX-Puro vector was employed as a negative control. For TCONS_00068220 gene downregulation, the specific small interfering RNA (si-TCONS_00068220) or Scrambled control shRNA (NC-siRNA) were provided by GenePharma Co. (Shanghai, China). The plasmids mentioned above were transfected into MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells via lentiviral vector-mediated transduction, following the standard protocol. After stably transfected cell lines were selected, cells were harvested and subjected to subsequent analysis.
RNA ISOLATION AND QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR:
Total RNA was extracted from tissues (n=60) or cultured cells using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). RNA was quantified and then immediately reverse-transcribed using the PrimeScript Reverse Transcription kit (TaKaRa, Dalian, China). Afterwards, quantitative PCR was carried out using SYBR Premix Ex Taq™ II (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) in an ABI 7500 RT-PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The primer sequences for TCONS_00068220 are as follows:
Data were normalized to the expression of endogenous GAPDH. The PCR protocol was conducted as follows: 5 min at 94°C, followed by 40 cycles of 15 s at 94°C and 1 min at 60°C. The relative quantity of DNA was calculated by the 2−ΔΔCt method. Each experiment was performed in triplicate.
CELL VIABILITY ASSAY:
A cell-counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay was performed to determine the viability of the cells. In brief, MCF-7 cells (2×103 cells/well) were plated into 96-well plates and incubated for 24 h at 37°C before conducting the assay. The cells were transfected with corresponding plasmids, and then 10 μL of CCK-8 solution (Solarbio, Beijing, China) was added to each well and cells were incubated for 1 h. The absorbance of samples was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
CELL MIGRATION AND INVASION ASSAY:
The migration and invasion potentials were measured 48 h after transfection using transwell chambers. For the cell migration assay, 8×104 cells were maintained in the upper chamber of 8 μm transwell microplates with serum-free DMEM medium (Corning Life Sciences, New York, NY, USA). For the invasion assay, cells were grown in the upper chamber precoated with 20% Matrigel (Corning Life Sciences). In both assays, DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS was added to the lower compartment. After incubation for 24 h, cells remaining on the upper side of the membrane were removed, and cells on the lower side were fixed in 4% methanol for 5 min and stained with 1% crystal violet for an additional 5 min at room temperature. Cells were observed and counted under an inverted microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
IN VIVO EXPERIMENTS:
Female BALB/c nude mice (aged 4–6 weeks; Central Laboratory of Animal Science, Jinan, Shandong) were raised under specific pathogen-free conditions. A total of 1×107 MDA-MB-231 cells with stable depletion of TCONS_00068220 (si-TCONS_00068220) or negative control (si-NC), or MCF-7 cells transfected with pLVX-TCONS_00068220 or pLVX-Puro, were injected subcutaneously into the left armpit of each mouse (n=6). Tumor dimensions were measured every 3 days using a caliper. Tumors were excised and weighed 21 days after inoculation. All in vivo procedures were performed with the NIH guide for the care and use of laboratory animals and were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Chinese Medicine Hospital of Tai’an City (No. 2020-08).
NUCLEUS AND CYTOPLASM ISOLATION:
Nuclear and cytosolic fractions were isolated using the Nuclei EZ Prep isolation kit (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). Nuclear RNA was then isolated from cytoplasmic RNA using centrifugation. The relative expression of TCONS_00068220 in the nucleus and the cytoplasm was detected by RT-PCR. GAPDH and U6 were used as internal reference genes for the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively.
RNA PULL-DOWN ASSAY:
Biotinylated TCONS_00068220 and negative control (GenePharma, Shanghai, China) were transfected into breast cancer cells. After 48-h transfection, 50 μL samples were divided into equal parts, and the remaining lysates were incubated with streptavidin agarose beads (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) for 1 h. This bead-administration method was described previously [17]. Ultimately, beads were boiled in sodium dodecyl sulfate buffer, and the eluted RNAs were detected by quantitative RT-PCR analysis.
WESTERN BLOT:
The harvested cells were pelleted and resuspended in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) lysis buffer (50 mM pH 6.8 Tris-HCl, 1% SDS, 10% glycerol, 20 mM DTT), followed by incubation on ice for further lysis, and were then centrifuged at 15 000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. Proteins were separated via 8% SDS-PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The membrane was blocked with 5% silk milk, and then incubated overnight at 4°C with mouse monoclonal primary antibodies against E-cadherin (1: 1000, #sc-21791), N-cadherin (1: 1000, #sc-59987), and beta-actin (1: 1000, #sc-47778) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA), followed by subsequent incubation with HRP-conjugated secondary goat anti-mouse IgG (1: 2000, #A0216, Beyotime, Shanghai, China) at room temperature for 1 hour. Then, the membrane was washed with PBST 3 times, followed by development using enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) reagents (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). Each experiment was performed in triplicate.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS:
Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) 19.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used to perform statistical analysis. Data were presented as mean±standard deviation. Comparison between 2 groups was conducted using a 2-tailed
Results
TCONS_00068220 IS UPREGULATED IN BREAST CANCER TISSUES:
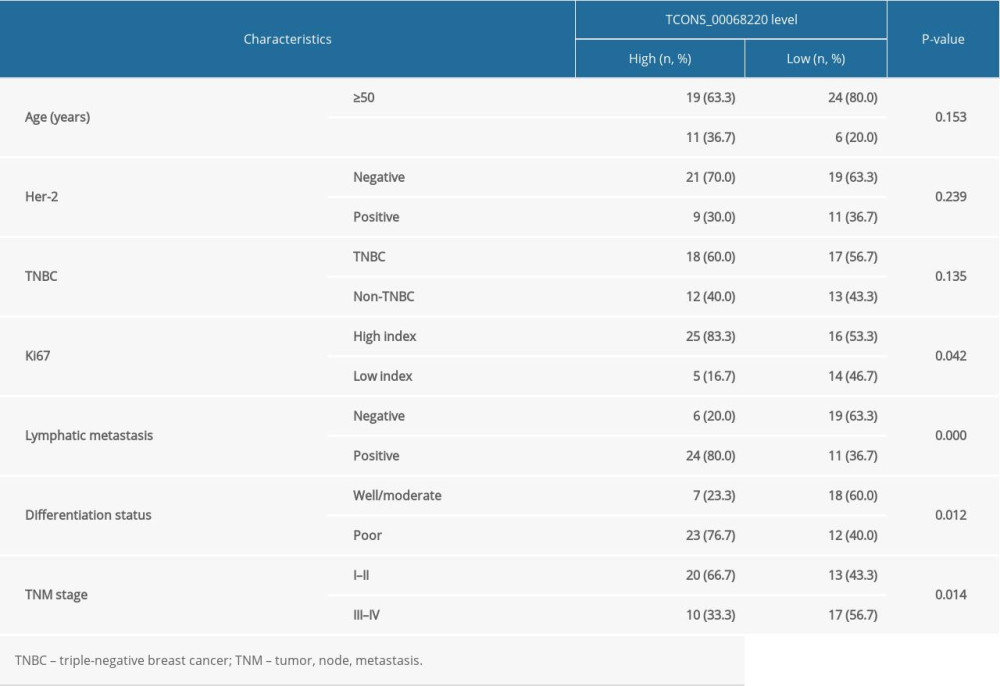
The relative expression levels of TCONS_00068220 in 60 paired breast cancer and adjacent non-cancerous tissue samples were assessed using qRT-PCR. As illustrated in Figure 1A, TCONS_00068220 expression was markedly elevated in breast cancer tissues (P=0.0086). To determine the correlation between TCONS_00068220 expression and traditional clinicopathological factors, the involved patients were divided into high and low groups, using the median TCONS_00068220 level in breast cancer tissues as the cut-off value. Although there was no apparent correlation between TCONS_00068220 expression and breast cancer subtype, TCONS_00068220 level was significantly associated with lymphatic metastasis, Ki67 index, clinical stage, and differentiation status (summarized in Table 1), suggestive of a significant role of TCONS_00068220 in breast cancer progression.
TCONS_00068220 EXPRESSION IS ELEVATED IN BREAST CANCER CELL LINES:
Next, we evaluated TCONS_00068220 expression in several different breast cancer cell lines. Compared with the normal breast epithelial cell line, TCONS_00068220 was clearly upregulated in all breast cancer cell lines, with MDA-MB-231 cells displaying the highest TCONS_00068220 expression, whereas MCF-7 cells showed the lowest TCONS_00068220 expression (Figure 1B; P=0.036, P=0.023, P=0.0091, P=0.0064). Thus, MDA-MB-231 was chosen to conduct the subsequent TCONS_00068220 gene knockdown experiments, while MCF-7 was suitable for TCONS_00068220 overexpression. Of note, the MDA-MB-231 cell line was previously identified to possess a high metastatic capacity [18,19], which implies that the overexpressed TCONS_00068220 gene may be associated with cell metastasis.
TCONS_00068220 PROMOTES BREAST CANCER CELL PROLIFERATION, MIGRATION, AND INVASION:
To verify this assumption, TCONS_00068220 was overexpressed in MCF-7 cells and silenced in MDA-MB-231 cells using lentiviral vector-mediated gene transduction, followed by the evaluation of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. The qRT-PCR results confirmed an increase in the expression of TCONS_00068220 in MCF-7 cells after transfection, whereas reduced TCONS_00068220 expression was observed in MDA-MB-231 cells with gene knockdown (Figure 2A; P=0.0051, P=0.0073). As expected, overexpression of TCONS_00068220 dramatically increased the viability of MCF-7 cells compared with the control cells, and downregulation of TCONS_00068220 suppressed MDA-MB-231 cell viability (P=0.031, Figure 2B).
In addition, the transwell assay demonstrated that the migratory and invasive behaviors of MCF-7 cells were significantly promoted due to TCONS_00068220 overexpression, while TCONS_00068220 knockdown in MDA-MB-231 cells led to a substantial decline in the number of migrated or invasive cells (P=0.019, P=0.015, P=0.017, P=0.011; Figure 2C, 2D).
TCONS_00068220 PROMOTES TUMOR GROWTH IN VIVO:
To further determine whether TCONS_00068220 affects the pathogenesis of breast cancer in vivo, we performed in vivo tumor growth assays. Stable TCONS_00068220-depleted MDA-MB-231 cells generated smaller xenograft tumors, reflected in the reduction in tumor weight and tumor volume (Figure 3A; P=0.0091, P=0.041, P=0.032, P=0.024, P=0.0075). The tumors derived from MCF-7 cells overexpressing TCONS_00068220 exhibited increased volumes and weights compared with those grown from control cells (Figure 3B; P=0.037, P=0.031, P=0.026, P=0.012, P=0.0098). These findings indicated that TCONS_00068220 can promote breast cancer proliferation in vivo.
TCONS_00068220 IS INVOLVED IN THE BREAST CANCER EPITHELIAL-MESENCHYMAL TRANSITION PROCESS:
After the in vivo tumor growth analysis, the expression profile of E-cadherin, an important marker in the process of EMT, was measured using immunoblot analysis. As shown in Figure 4A, the protein level of E-cadherin was clearly decreased in MCF-7 cells overexpressing TCONS_00068220 compared with control cells. On the contrary, when MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with siRNA against TCONS_00068220, the expression of E-cadherin was remarkably amplified.
E-CADHERIN WAS DOWNREGULATED IN BREAST CANCER CELLS:
Among the above-mentioned EMT markers, we focused on the expression pattern of E-cadherin in breast cancer. As shown in Figure 4B, E-cadherin was downregulated in breast cancer tissues (P=0.0054). In addition, E-cadherin level was negatively correlated with that of TCONS_00068220 (Figure 4C, P=0.00089). In contrast with TCONS_00068220, E-cadherin was expressed at the highest level in MCF-7 cells and the lowest in MDA-MB-231 cells (Figure 4D, P=0.036, P=0.0081, P=0035, P=0.0053).
TCONS00068220 INHIBITS E-CADHERIN GENE TRANSCRIPTION:
The functional role of lncRNAs in cancer cells largely depends on their subcellular localization. In this context, we performed a nucleus-cytoplasm isolation assay to further elucidate the molecular mechanism by which TCONS_00068220 regulates E-cadherin expression. Results indicated that TCONS_00068220 was distributed in both the nucleus and cytoplasm but was expressed in relative abundance in the cytoplasm (Figure 5A). Cytoplasmic lncRNAs can sometimes modulate gene transcription through interaction with the target genes. The RNA pull-down results showed that TCONS_00068220 bound directly to E-cadherin mRNA in both MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells (Figure 5B; P=0.035, P=0.043).
TCONS_00068220 REGULATED BREAST CANCER CELL PERFORMANCE BY SUPPRESSING E-CADHERIN:
Next, we employed rescue experiments to confirm whether TCONS_00068220 modulated cell behaviors through downregulating E-cadherin gene expression. As illustrated in Figure 6A, E-cadherin level was remarkably decreased in MCF-7 cells transfected with TCONS_00068220 while the compromised E-cadherin expression was significantly abated by co-transfection with pcDNA3.1-E-cadherin (P=0.023, P=0.033, P=0.037). Our results also indicated that E-cadherin silencing in MDA-MB-231 mitigated the elevated E-cadherin level caused by TCONS_00068220 knockdown (P=0.022, P=0.015, P=0.042). Furthermore, enhanced expression of E-cadherin abrogated the effect of TCONS_00068220 overexpression on MCF-7 cell proliferation, migration, and invasion (Figure 6B–6D). Likewise, TCONS_00068220 knockdown-mediated suppression of malignant behavior in MDA-MB-231 cells was restored after E-cadherin silencing. All these data suggest that TCONS_00068220 suppresses the expression of its target gene E-cadherin, which induces EMT, and thereby promotes tumorigenesis.
Discussion
Despite the great efforts made in breast cancer diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, most patients are generally diagnosed at an advanced stage; hence, unfavorable outcomes await these patients [20]. Furthermore, tumors become increasingly aggressive as a result of gradual accumulation of genetic alterations or mutations [21,22]. It is imperative to further understand the molecular mechanisms of breast cancer progression.
As a novel class of noncoding RNA molecules, lncRNAs have attracted researchers’ attention in the field of oncology in recent years. lncRNAs are implicated in the modulation of numerous pathological processes related to cancer development, including angiogenesis, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, differentiation, migration, and invasion, as well as reprogramming of pluripotent stem cells [23,24]. Emerging evidence reveals that lncRNAs function as drivers of tumor suppressors or oncogenes, thus playing an essential role in regulating numerous cancers [25–27]. Through microarray analysis, lncRNA TCONS_00068220 was previously identified to be differentially expressed in gastric cancer tissues and co-expressed with interleukin-7 [15], a putative tumor suppressor which can mitigate tumor growth and induce complete regression [28], indicating a significant role for TCONS_00068220 in tumor pathogenesis. In accordance with these findings, Zhao et al confirmed that TCONS_00068220 was upregulated in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines using qRT-PCR, and found that TCONS_00068220 gene silencing inhibited gastric cancer cell viability and induced cell apoptosis [16]. Together, these findings demonstrate that TCONS_00068220 acts as an oncogene in gastric carcinoma. However, few studies have elucidated the effect of lncRNA TCONS_00068220 on other types of cancer. In the present study, the level of TCONS_00068220 was notably increased in breast cancer tissues in comparison with adjacent non-cancerous tissues. TCONS_00068220 was also clearly augmented in several different breast cancer cell lines compared with normal breast epithelial cells. Besides, a high expression level of TCONS_00068220 was associated with tumor metastasis, high Ki67 index, advanced TNM stages, and low differentiation grade. These results suggest that dysregulated expression of TCONS_00068220 may contribute to increased breast cancer malignancy.
Indeed, we observed that the proliferation of MCF-7 cells was significantly increased in response to enhanced expression of TCONS_00068220 while MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation was dramatically inhibited after TCONS_00068220 gene knockdown. This was strictly consistent with a previous study reporting that TCONS_00068220 suppresses cancer cell proliferation [16]. Moreover, migratory and invasive phenotypes were more apparent in cells with TCONS_00068220 overexpression. In contrast, migrated or invasive cells were substantially decreased following TCONS_00068220 depletion, which might explain the correlation between high TCONS_00068220 expression and lymphatic metastasis in patients with breast cancer.
EMT is well recognized as a hallmark of cell invasiveness, and endows tumor cells with stem cell-like characteristics, such as immortalized proliferation and distant metastasis [29]. Previous studies have reported that various lncRNAs are involved in regulating the EMT process, which leads to cancer development [30,31]. For instance, it has been recently reported that upregulation of lncRNA CASC9 promotes tumorigenesis by affecting EMT and is responsible for undesirable prognosis in patients [32]. NEAT1 facilitates cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by stimulating EMT in breast cancer [33]. Zheng and coworkers also confirmed that RHPN1-AS1 contributes to tumor progression by enhancing the EMT process [34]. Additionally, we conducted western blot analysis to measure the expression profiles of the EMT marker proteins, and found that overexpression of TCONS_00068220 suppressed the protein expression of epithelial marker E-cadherin, whereas the opposite results were obtained in TCONS_00068220-depleted cells. Taken together, our results indicate that TCONS_00068220 promotes the process of EMT during breast cancer progression.
LncRNAs exert regulatory functions via various mechanisms, such as epigenetic silencing, modulation of mRNA stability, and even interaction with miRNA as ‘sponge RNAs’ [35–37]. In our study, the subcellular localization of TCONS_00068220 was determined by performing a nucleus-cytoplasm isolation assay, and the results demonstrated that it was expressed in relative abundance in the cytoplasm of breast cancer cells. The RNA pull-down assay indicated that TCONS_00068220 bound directly to E-cadherin mRNA. In fact, altered expression of E-cadherin abrogated the effect of TCONS_00068220 on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, suggesting that the function of TCONS_00068220 in regulating malignant cell behaviors largely depends on the modulation of E-cadherin expression.
Conclusions
In conclusion, our data indicate that upregulation of lncRNA TCONS_00068220 in breast cancer inhibits the expression of E-cadherin protein and therefore promotes cancer progression by, at least in part, enhancing the process of EMT. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that TCONS_00068220 has been identified to function as a novel oncogene in breast cancer development, although further mechanistic investigations remain to be carried out.
Figures
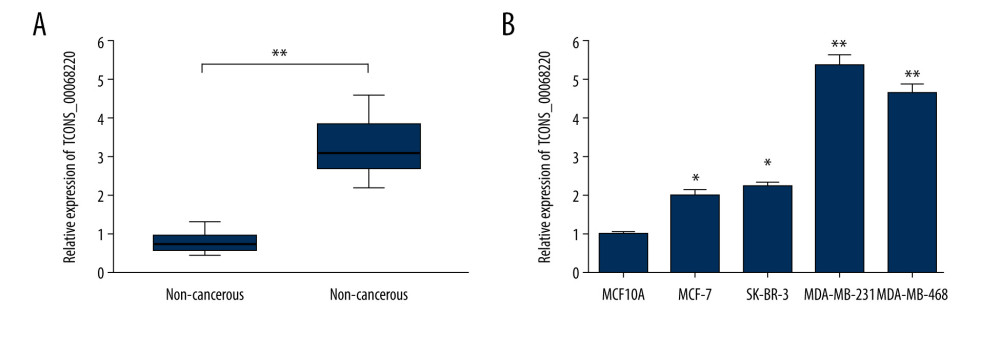 Figure 1. TCONS_00068220 was upregulated in breast cancer. (A) The relative level of TCONS_00068220 was measured in breast cancer tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues using qRT-PCR. (B) The relative levels of TCONS_00068220 in various breast cancer cell lines were assessed through qRT-PCR. * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control.
Figure 1. TCONS_00068220 was upregulated in breast cancer. (A) The relative level of TCONS_00068220 was measured in breast cancer tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues using qRT-PCR. (B) The relative levels of TCONS_00068220 in various breast cancer cell lines were assessed through qRT-PCR. * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control. 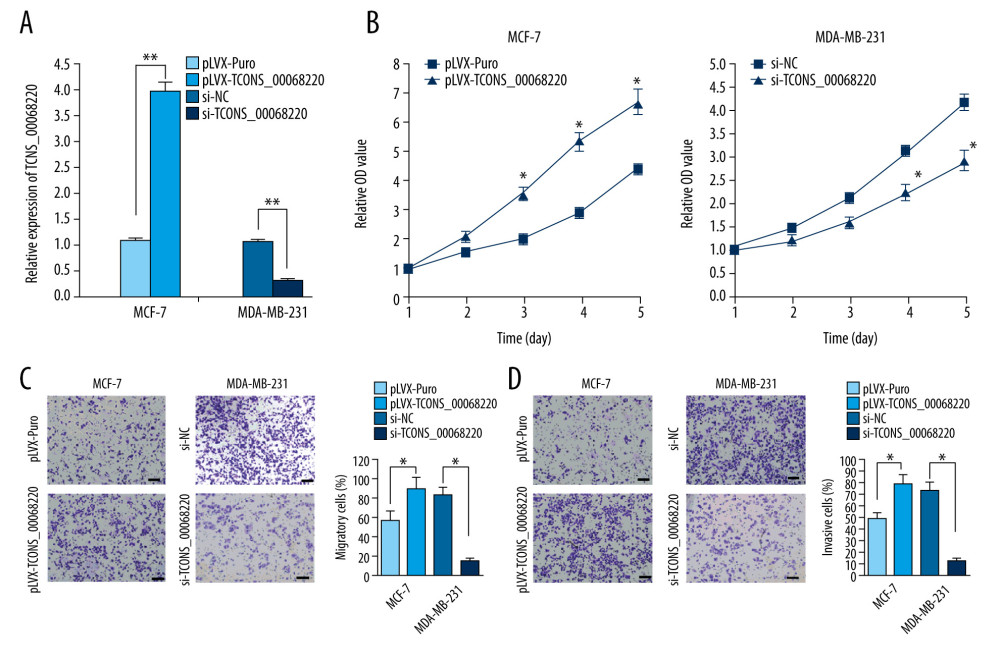 Figure 2. TCONS_00068220 modulates aggressive behaviors in breast cancer cells. TCONS_00068220 was overexpressed in the MCF-7 cell line and silenced in the MDA-MB-231 cell line via lentiviral vector-mediated transduction. (A) Verification of the efficiency of TCONS_00068220 overexpression or knockdown via qRT-PCR. (B) Cell proliferation was evaluated using a CCK8 assay after TCONS_00068220 overexpression or silencing. A transwell assay showed the effects of TCONS_00068220 expression alterations on cell migration (C) and invasion (D). * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control group.
Figure 2. TCONS_00068220 modulates aggressive behaviors in breast cancer cells. TCONS_00068220 was overexpressed in the MCF-7 cell line and silenced in the MDA-MB-231 cell line via lentiviral vector-mediated transduction. (A) Verification of the efficiency of TCONS_00068220 overexpression or knockdown via qRT-PCR. (B) Cell proliferation was evaluated using a CCK8 assay after TCONS_00068220 overexpression or silencing. A transwell assay showed the effects of TCONS_00068220 expression alterations on cell migration (C) and invasion (D). * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control group. 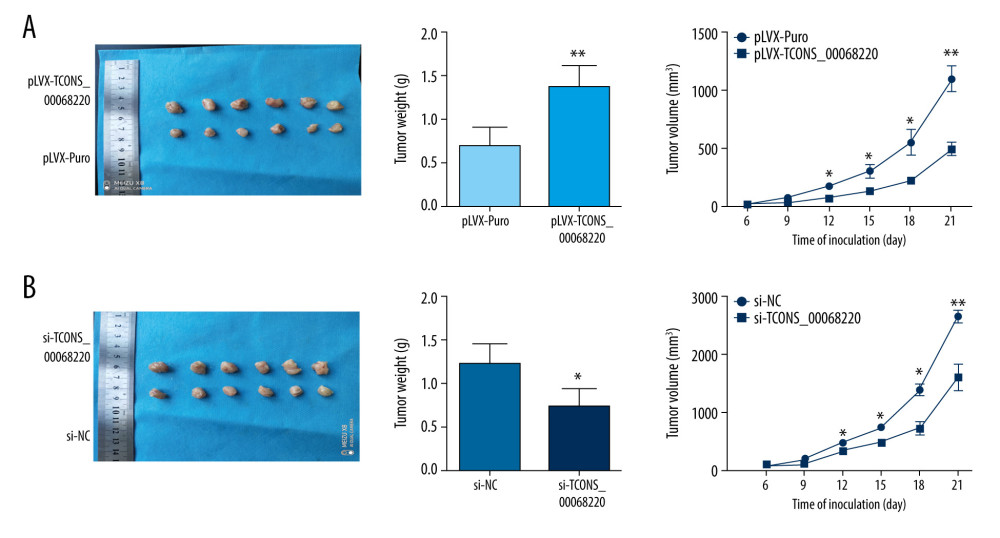 Figure 3. TCONS_00068220 promotes breast cancer cell growth in vivo. (A) Effects of TCONS_00068220 knockdown on tumor growth in vivo. Left: Representative images of tumors formed in nude mice injected subcutaneously with the TCONS_00068220-depleted MDA-MB-231 cells. Middle: tumor weights. Right: tumor volumes. Tumors derived from cells with TCONS_00068220 overexpression were substantially smaller than the control group. (B) Effects of TCONS_00068220 overexpression on tumor growth in vivo. Left: Representative images of tumors formed in nude mice injected subcutaneously with MCF-7 cells overexpressing TCONS_00068220. The tumor weight (middle) and tumor volume (right) were markedly increased in the pLVX-TCONS_00068220 group compared with the control group. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01.
Figure 3. TCONS_00068220 promotes breast cancer cell growth in vivo. (A) Effects of TCONS_00068220 knockdown on tumor growth in vivo. Left: Representative images of tumors formed in nude mice injected subcutaneously with the TCONS_00068220-depleted MDA-MB-231 cells. Middle: tumor weights. Right: tumor volumes. Tumors derived from cells with TCONS_00068220 overexpression were substantially smaller than the control group. (B) Effects of TCONS_00068220 overexpression on tumor growth in vivo. Left: Representative images of tumors formed in nude mice injected subcutaneously with MCF-7 cells overexpressing TCONS_00068220. The tumor weight (middle) and tumor volume (right) were markedly increased in the pLVX-TCONS_00068220 group compared with the control group. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01. 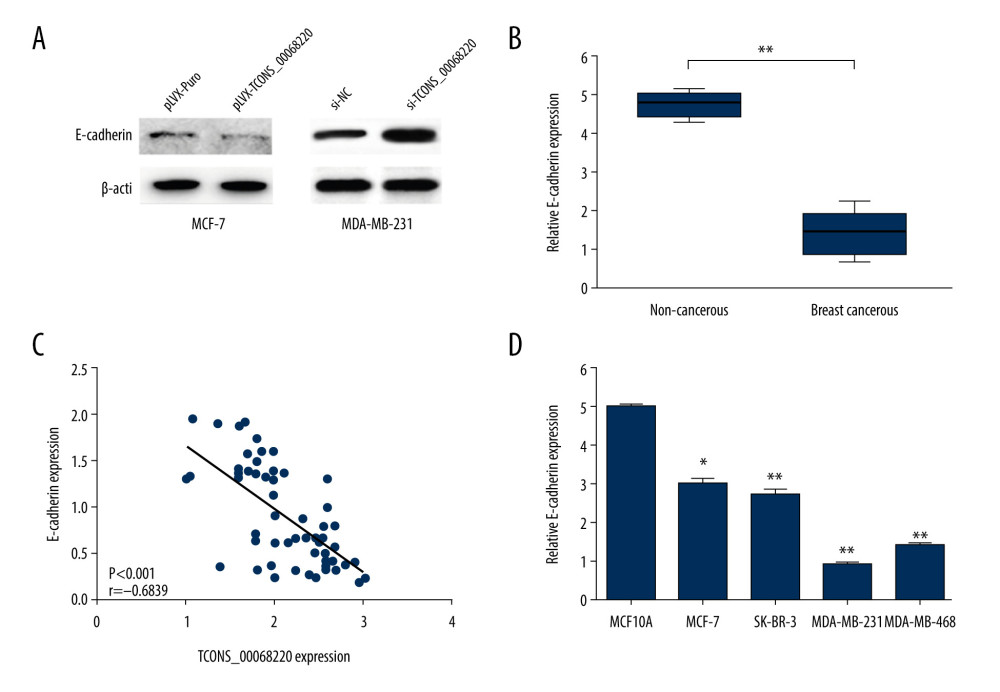 Figure 4. TCONS_00068220 promotes EMT and E-cadherin was downregulated in breast cancer. (A) Western blot assay was used to evaluate the protein expression of EMT markers in response to TCONS_00068220 overexpression in MCF-7 cells or knockdown in MDA-MB-231 cells. (B) E-cadherin level in breast cancer and adjacent normal tissues. (C) Negative correlation between expression levels of TCONS_00068220 and E-cadherin in breast cancer tissues. (D) E-cadherin level in MCF10A and various breast cancer cells. EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition. * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control.
Figure 4. TCONS_00068220 promotes EMT and E-cadherin was downregulated in breast cancer. (A) Western blot assay was used to evaluate the protein expression of EMT markers in response to TCONS_00068220 overexpression in MCF-7 cells or knockdown in MDA-MB-231 cells. (B) E-cadherin level in breast cancer and adjacent normal tissues. (C) Negative correlation between expression levels of TCONS_00068220 and E-cadherin in breast cancer tissues. (D) E-cadherin level in MCF10A and various breast cancer cells. EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition. * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control. 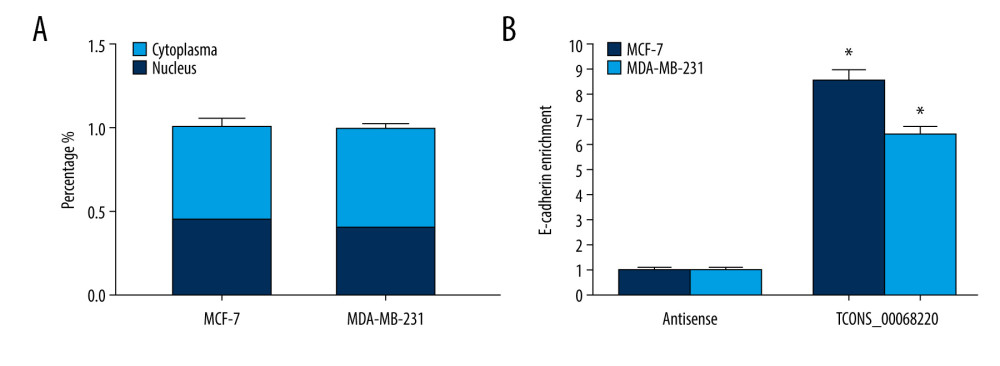 Figure 5. TCONS_00068220 directly interacts with E-cadherin. (A) TCONS_00068220 subcellular localization detected by the nucleus and cytoplasm isolation assay. (B) Biotinylated TCONS_00068220 and its antisense sequence were incubated with MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231cell lysates, respectively, targeted with streptavidin beads, washed, and bound RNAs were subjected to PCR analysis. * P<0.05 vs control.
Figure 5. TCONS_00068220 directly interacts with E-cadherin. (A) TCONS_00068220 subcellular localization detected by the nucleus and cytoplasm isolation assay. (B) Biotinylated TCONS_00068220 and its antisense sequence were incubated with MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231cell lysates, respectively, targeted with streptavidin beads, washed, and bound RNAs were subjected to PCR analysis. * P<0.05 vs control. 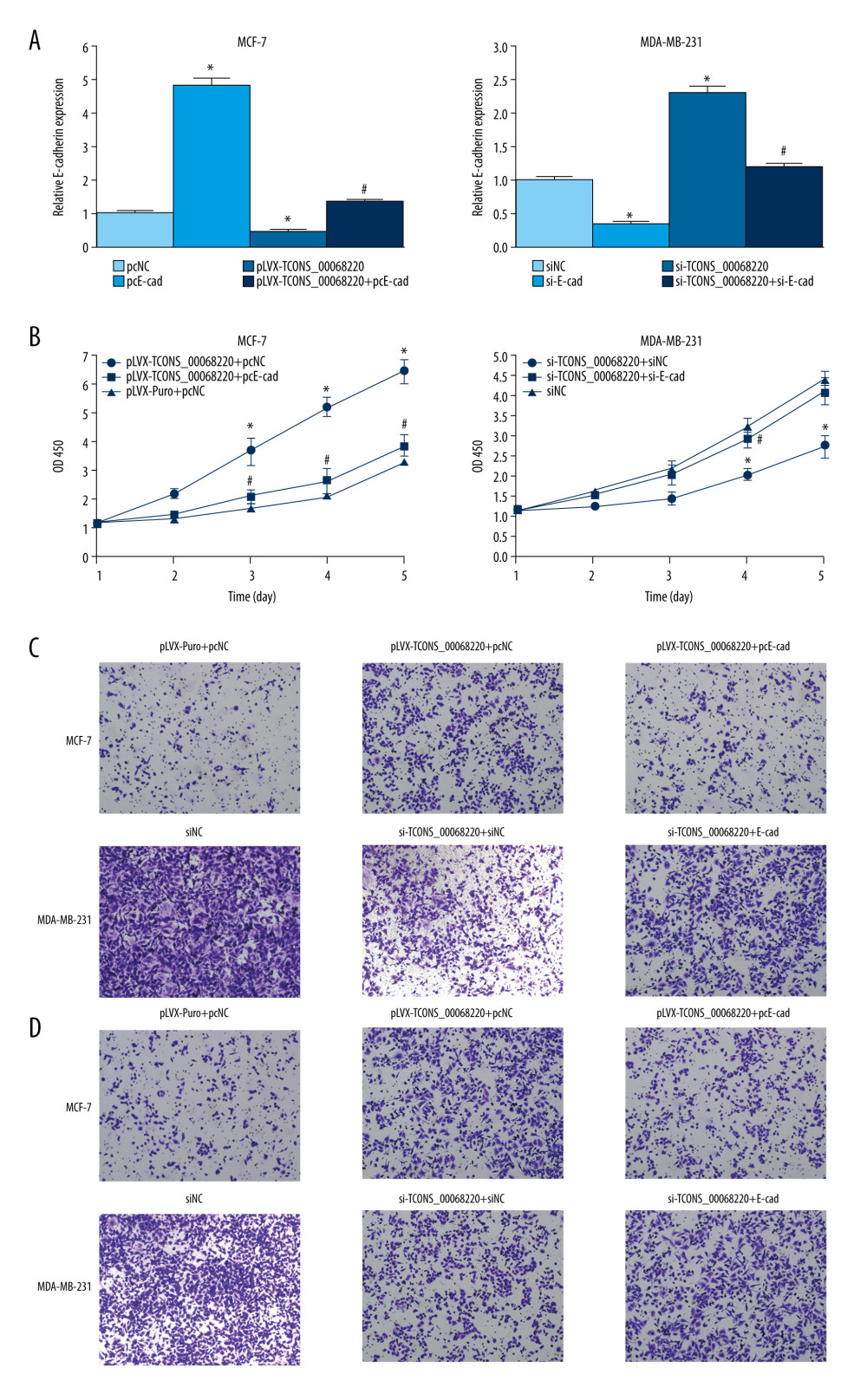 Figure 6. TCONS_00068220 modulates breast cancer cell performance by downregulating E-cadherin. E-cadherin was overexpressed in pLVX-TCONS_00068220-transfected MCF-7 cells, while E-cadherin was silenced in MDA-MB-231 cells with TCONS_00068220 knockdown. (A) Assessment of the overexpression of E-cadherin by using qRT-PCR. (B) Cell viability was evaluated using the CCK8 assay. (C) Cell migration was measured by transwell assay. (D) Cell invasion was tested by Matrigel transwell assay. * P<0.05 vs negative control (NC) group; # P<0.05 vs pLVX-TCONS_00068220+pcDNA3.1-NC group or si-TCONS_00068220+si-NC.
Figure 6. TCONS_00068220 modulates breast cancer cell performance by downregulating E-cadherin. E-cadherin was overexpressed in pLVX-TCONS_00068220-transfected MCF-7 cells, while E-cadherin was silenced in MDA-MB-231 cells with TCONS_00068220 knockdown. (A) Assessment of the overexpression of E-cadherin by using qRT-PCR. (B) Cell viability was evaluated using the CCK8 assay. (C) Cell migration was measured by transwell assay. (D) Cell invasion was tested by Matrigel transwell assay. * P<0.05 vs negative control (NC) group; # P<0.05 vs pLVX-TCONS_00068220+pcDNA3.1-NC group or si-TCONS_00068220+si-NC. References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A, Cancer statistics, 2020: Cancer J Clin, 2020; 70; 7-30
2. Daniels B, Kiely BE, Lord SJ, Long-term survival in trastuzumab-treated patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: Real-world outcomes and treatment patterns in a whole-of-population Australian cohort (2001–2016): Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2018; 171; 151-59
3. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries: Cancer J Clin, 2018; 68; 394-424
4. Zhao L, Zhou S, Gustafsson JA, Nuclear receptors: Recent drug discovery for cancer therapies: Endocr Rev, 2019; 40; 1207-49
5. Waterhouse MP, Ugur R, Khaled WT, Therapeutic and mechanistic perspectives of protein complexes in breast cancer: Front Cell Dev Biol, 2019; 7; 335
6. Huarte M, The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer: Nat Med, 2015; 21; 1253-61
7. Groen JN, Capraro D, Morris KV, The emerging role of pseudogene expressed non-coding RNAs in cellular functions: Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2014; 54; 350-55
8. Sun M, Liu X, Xia L, A nine-lncRNA signature predicts distant relapse-free survival of HER2-negative breast cancer patients receiving taxane and anthracycline-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Biochem Pharmacol, 2020 [Online ahead of print]
9. Chen X, Yang J, Qian L, Cao T, Aberrantly expressed mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in patients with invasive ductal breast carcinoma: a pilot study: Mol Med Rep, 2015; 11; 2185-90
10. Sun M, Gadad SS, Kim DS, Kraus WL, Discovery, annotation, and functional analysis of long noncoding RNAs controlling cell-cycle gene expression and proliferation in breast cancer cells: Mol Cell, 2015; 59; 698-711
11. Peng F, Li TT, Wang KL, H19/let-7/LIN28 reciprocal negative regulatory circuit promotes breast cancer stem cell maintenance: Cell Death Dis, 2017; 8; e2569
12. Zeng H, Wang J, Chen T, Downregulation of long non-coding RNA Opa interacting protein 5-antisense RNA 1 inhibits breast cancer progression by targeting sex-determining region Y-box 2 by microRNA-129-5p upregulation: Cancer Sci, 2019; 110; 289-302
13. Zhang J, Zhang P, Wang L, Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in carcinogenesis and metastasis: Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2014; 46; 1-5
14. Sang Y, Tang J, Li S, LncRNA PANDAR regulates the G1/S transition of breast cancer cells by suppressing p16(INK4A) expression: Sci Rep, 2016; 6; 22366
15. Zhao Z, Song Y, Piao D, Identification of genes and long non-coding RNAs associated with the pathogenesis of gastric cancer: Oncol Rep, 2015; 34; 1301-10
16. Zhao Z, Xue J, Song Y, Liu T, Piao D, Downregulated long non-coding RNA TCONS_00068220 upregulates apoptosis in gastric cancer cells: Oncol Lett, 2017; 14; 6143-50
17. Su JC, Hu XF, Long noncoding RNA HOXA11AS promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in human breast cancer: Mol Med Rep, 2017; 16; 4887-94
18. Zhou P, Liu P, Zhang J, Long noncoding RNA RUSC1ASN promotes cell proliferation and metastasis through Wnt/beta catenin signaling in human breast cancer: Mol Med Rep, 2019; 19; 861-68
19. Meissner HI, Klabunde CN, Han PK, Breast cancer screening beliefs, recommendations and practices: Primary care physicians in the United States: Cancer-Am Cancer Soc, 2011; 117; 3101-11
20. Lee EY, Muller WJ, Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes: Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2010; 2; a3236
21. Bandini E, Fanini F, Vannini I, miR-9-5p as a regulator of the androgen receptor pathway in breast cancer cell lines: Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020; 8; 579160
22. Li T, Yang Z, Jiang S, Melatonin: Does it have utility in the treatment of haematological neoplasms?: Br J Pharmacol, 2018; 175; 3251-62
23. Hu P, Chu J, Wu Y, NBAT1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis by regulating DKK1 via PRC2: Oncotarget, 2015; 6; 32410-25
24. Bao J, Yu Y, Chen J, MiR-126 negatively regulates PLK-4 to impact the development of hepatocellular carcinoma via ATR/CHEK1 pathway: Cell Death Dis, 2018; 9; 1045
25. Xue C, He Y, Hu Q, Downregulation of PIM1 regulates glycolysis and suppresses tumor progression in gallbladder cancer: Cancer Manag Res, 2018; 10; 5101-12
26. Chen J, Yu Y, Chen X, MiR-139-5p is associated with poor prognosis and regulates glycolysis by repressing PKM2 in gallbladder carcinoma: Cell Prolif, 2018; 51; e12510
27. Vicari A, de Moraes MC, Gombert JM, Interleukin 7 induces preferential expansion of V beta 8.2+CD4–8- and V beta 8.2+CD4+8- murine thymocytes positively selected by class I molecules: J Exp Med, 1994; 180; 653-61
28. Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA, Thiery JP, EMT 2016: Cell, 2016; 166; 21-45
29. Lei H, Gao Y, Xu X, LncRNA TUG1 influences papillary thyroid cancer cell proliferation, migration and EMT formation through targeting miR-145: Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2017; 49; 588-97
30. Liang G, Fang X, Yang Y, Song Y, Silencing of CEMIP suppresses Wnt/beta-catenin/Snail signaling transduction and inhibits EMT program of colorectal cancer cells: Acta Histochem, 2018; 120; 56-63
31. Gao GD, Liu XY, Lin Y, LncRNA CASC9 promotes tumorigenesis by affecting EMT and predicts poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell cancer: Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018; 22; 422-29
32. Zhang M, Wu WB, Wang ZW, Wang XH, lncRNA NEAT1 is closely related with progression of breast cancer via promoting proliferation and EMT: Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2017; 21; 1020-26
33. Zheng S, Lv P, Su J, Miao K, Xu H, Li M, Silencing of the long non-coding RNA RHPN1-AS1 suppresses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inhibits breast cancer progression: Am J Transl Res, 2019; 11; 3505-17
34. Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I, A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA: Cell, 2011; 147; 358-69
35. Xing Z, Lin A, Li C, lncRNA directs cooperative epigenetic regulation downstream of chemokine signals: Cell, 2014; 159; 1110-25
36. Heo JB, Sung S, Vernalization-mediated epigenetic silencing by a long intronic noncoding RNA: Science, 2011; 331; 76-79
Figures
 Figure 1. TCONS_00068220 was upregulated in breast cancer. (A) The relative level of TCONS_00068220 was measured in breast cancer tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues using qRT-PCR. (B) The relative levels of TCONS_00068220 in various breast cancer cell lines were assessed through qRT-PCR. * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control.
Figure 1. TCONS_00068220 was upregulated in breast cancer. (A) The relative level of TCONS_00068220 was measured in breast cancer tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues using qRT-PCR. (B) The relative levels of TCONS_00068220 in various breast cancer cell lines were assessed through qRT-PCR. * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control. Figure 2. TCONS_00068220 modulates aggressive behaviors in breast cancer cells. TCONS_00068220 was overexpressed in the MCF-7 cell line and silenced in the MDA-MB-231 cell line via lentiviral vector-mediated transduction. (A) Verification of the efficiency of TCONS_00068220 overexpression or knockdown via qRT-PCR. (B) Cell proliferation was evaluated using a CCK8 assay after TCONS_00068220 overexpression or silencing. A transwell assay showed the effects of TCONS_00068220 expression alterations on cell migration (C) and invasion (D). * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control group.
Figure 2. TCONS_00068220 modulates aggressive behaviors in breast cancer cells. TCONS_00068220 was overexpressed in the MCF-7 cell line and silenced in the MDA-MB-231 cell line via lentiviral vector-mediated transduction. (A) Verification of the efficiency of TCONS_00068220 overexpression or knockdown via qRT-PCR. (B) Cell proliferation was evaluated using a CCK8 assay after TCONS_00068220 overexpression or silencing. A transwell assay showed the effects of TCONS_00068220 expression alterations on cell migration (C) and invasion (D). * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control group. Figure 3. TCONS_00068220 promotes breast cancer cell growth in vivo. (A) Effects of TCONS_00068220 knockdown on tumor growth in vivo. Left: Representative images of tumors formed in nude mice injected subcutaneously with the TCONS_00068220-depleted MDA-MB-231 cells. Middle: tumor weights. Right: tumor volumes. Tumors derived from cells with TCONS_00068220 overexpression were substantially smaller than the control group. (B) Effects of TCONS_00068220 overexpression on tumor growth in vivo. Left: Representative images of tumors formed in nude mice injected subcutaneously with MCF-7 cells overexpressing TCONS_00068220. The tumor weight (middle) and tumor volume (right) were markedly increased in the pLVX-TCONS_00068220 group compared with the control group. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01.
Figure 3. TCONS_00068220 promotes breast cancer cell growth in vivo. (A) Effects of TCONS_00068220 knockdown on tumor growth in vivo. Left: Representative images of tumors formed in nude mice injected subcutaneously with the TCONS_00068220-depleted MDA-MB-231 cells. Middle: tumor weights. Right: tumor volumes. Tumors derived from cells with TCONS_00068220 overexpression were substantially smaller than the control group. (B) Effects of TCONS_00068220 overexpression on tumor growth in vivo. Left: Representative images of tumors formed in nude mice injected subcutaneously with MCF-7 cells overexpressing TCONS_00068220. The tumor weight (middle) and tumor volume (right) were markedly increased in the pLVX-TCONS_00068220 group compared with the control group. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01. Figure 4. TCONS_00068220 promotes EMT and E-cadherin was downregulated in breast cancer. (A) Western blot assay was used to evaluate the protein expression of EMT markers in response to TCONS_00068220 overexpression in MCF-7 cells or knockdown in MDA-MB-231 cells. (B) E-cadherin level in breast cancer and adjacent normal tissues. (C) Negative correlation between expression levels of TCONS_00068220 and E-cadherin in breast cancer tissues. (D) E-cadherin level in MCF10A and various breast cancer cells. EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition. * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control.
Figure 4. TCONS_00068220 promotes EMT and E-cadherin was downregulated in breast cancer. (A) Western blot assay was used to evaluate the protein expression of EMT markers in response to TCONS_00068220 overexpression in MCF-7 cells or knockdown in MDA-MB-231 cells. (B) E-cadherin level in breast cancer and adjacent normal tissues. (C) Negative correlation between expression levels of TCONS_00068220 and E-cadherin in breast cancer tissues. (D) E-cadherin level in MCF10A and various breast cancer cells. EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition. * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 vs control. Figure 5. TCONS_00068220 directly interacts with E-cadherin. (A) TCONS_00068220 subcellular localization detected by the nucleus and cytoplasm isolation assay. (B) Biotinylated TCONS_00068220 and its antisense sequence were incubated with MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231cell lysates, respectively, targeted with streptavidin beads, washed, and bound RNAs were subjected to PCR analysis. * P<0.05 vs control.
Figure 5. TCONS_00068220 directly interacts with E-cadherin. (A) TCONS_00068220 subcellular localization detected by the nucleus and cytoplasm isolation assay. (B) Biotinylated TCONS_00068220 and its antisense sequence were incubated with MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231cell lysates, respectively, targeted with streptavidin beads, washed, and bound RNAs were subjected to PCR analysis. * P<0.05 vs control. Figure 6. TCONS_00068220 modulates breast cancer cell performance by downregulating E-cadherin. E-cadherin was overexpressed in pLVX-TCONS_00068220-transfected MCF-7 cells, while E-cadherin was silenced in MDA-MB-231 cells with TCONS_00068220 knockdown. (A) Assessment of the overexpression of E-cadherin by using qRT-PCR. (B) Cell viability was evaluated using the CCK8 assay. (C) Cell migration was measured by transwell assay. (D) Cell invasion was tested by Matrigel transwell assay. * P<0.05 vs negative control (NC) group; # P<0.05 vs pLVX-TCONS_00068220+pcDNA3.1-NC group or si-TCONS_00068220+si-NC.
Figure 6. TCONS_00068220 modulates breast cancer cell performance by downregulating E-cadherin. E-cadherin was overexpressed in pLVX-TCONS_00068220-transfected MCF-7 cells, while E-cadherin was silenced in MDA-MB-231 cells with TCONS_00068220 knockdown. (A) Assessment of the overexpression of E-cadherin by using qRT-PCR. (B) Cell viability was evaluated using the CCK8 assay. (C) Cell migration was measured by transwell assay. (D) Cell invasion was tested by Matrigel transwell assay. * P<0.05 vs negative control (NC) group; # P<0.05 vs pLVX-TCONS_00068220+pcDNA3.1-NC group or si-TCONS_00068220+si-NC. In Press
12 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Comparing Neuromuscular Blockade Measurement Between Upper Arm (TOF Cuff®) and Eyelid (TOF Scan®) Using Miv...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943630
11 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Enhancement of Frozen-Thawed Human Sperm Quality with Zinc as a Cryoprotective AdditiveMed Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942946
12 Mar 2024 : Database Analysis
Risk Factors of Age-Related Macular Degeneration in a Population-Based Study: Results from SHIP-TREND-1 (St...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943140
12 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Preoperative Blood Transfusion Requirements for Hemorrhoidal Severe Anemia: A Retrospective Study of 128 Pa...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943126
Most Viewed Current Articles
17 Jan 2024 : Review article
Vaccination Guidelines for Pregnant Women: Addressing COVID-19 and the Omicron VariantDOI :10.12659/MSM.942799
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942799
14 Dec 2022 : Clinical Research
Prevalence and Variability of Allergen-Specific Immunoglobulin E in Patients with Elevated Tryptase LevelsDOI :10.12659/MSM.937990
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e937990
16 May 2023 : Clinical Research
Electrophysiological Testing for an Auditory Processing Disorder and Reading Performance in 54 School Stude...DOI :10.12659/MSM.940387
Med Sci Monit 2023; 29:e940387
01 Jan 2022 : Editorial
Editorial: Current Status of Oral Antiviral Drug Treatments for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Non-Hospitalized Pa...DOI :10.12659/MSM.935952
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e935952