25 December 2020: Clinical Research
Elevated CA-125 Level and ER-Negative as Prognostic Factors for Ovarian Metastasis in Patients with Endometrial Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Xiaoting Ling1ABCE, Zheyu Zheng2ABCE, Jing Xu1C, Guocai Xu1F, Hui Zhou1CD, Zhongqiu Lin1F, Yangyang Li3BDE, Jinxiao Liang1AG, Huaiwu Lu1AD*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.928826
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e928826
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The utility of cancer antigen 125 (CA-125), estrogen receptor (ER), and progesterone receptor (PR) in evaluation for ovarian metastasis of endometrial cancer has yet to be determined. The purpose of this study was to investigate the incidence and the possible risk factors of ovarian metastasis.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: A retrospective study was performed in endometrial cancer patients who accepted surgical intervention of hysterectomy and oophorectomy during 2002–2013 in Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, China. Clinico-pathologic characteristics and the possible risk factors were investigated.
RESULTS: A total of 565 patients were identified, of which 5.7% had ovarian metastasis. Univariate analysis and multivariate analysis revealed that deeper myometrial invasion, tubal involvement, and parametrial involvement were independent risk factors. In subgroup analysis, univariate analysis showed that elevated CA-125 level and negative ER were associated with ovarian metastasis (P<0.05), however multivariate analysis revealed that only high CA-125 level was an independent risk factor (P<0.05). The incidence of ovarian metastasis in patients with high CA-125 level and who were ER-negative was 24%. For patients with normal CA-125 level and who were ER-positive, the incidence was 1.19%. The optimal cutoff value that provided the best sensitivity and specificity was 110.5 U/ml.
CONCLUSIONS: The incidence of ovarian metastasis in endometrial cancer is low. Ovarian preservation should be considered for women without abnormal CA-125 level and who have deeper myometrial invasion, tubal involvement, parametrial involvement, and who are ER-negative. These findings may facilitate clinical decision-making.
Keywords: Endometrial Neoplasms, Ovariectomy, CA-125 Antigen, Multivariate Analysis, Ovarian Neoplasms, ROC Curve, Receptors, Estrogen, Receptors, Progesterone, Risk Factors
Background
The standard treatment for endometrial cancer includes removing the ovaries to reduce estrogen production [1]. However, the effects of bilateral oophorectomy on the short-term and long-term health of young patients may include cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and cognitive decline. Atsma et al. reported a risk ratio of 2.62 [95% confidence interval (CI), 2.05–3.35] for cardiovascular disease in patients with bilateral oophorectomy [2]. Rocca et al. found that the mortality risk was increased by 67% (hazard ratio (HR) to 1.67 [95% CI 1.16–2.40]
Preservation of ovaries in young women with endometrial cancer remains controversial [2]. Some reports have demonstrated that preservation of the ovaries is safe in patients with early-stage EC [4]. However, the incidence of metastatic ovarian cancer and coexisting malignancies in endometrial cancer varies from 5% to 29% [5–10]. Therefore, the decision to preserve the ovaries must be carefully considered.
Although prior reports have examined the risk factors associated with ovarian metastasis in patients with EC, reliable preoperative risk factors have not been conclusively demonstrated. Preoperative images may help estimate the predictive factors such as deeper myometrial invasion, lymph node status, and tumor size, but all of these factors need to be confirmed after surgery.
Therefore, an accurate measurement of clinical factors before treatment may be more important. Preoperative elevated CA-125 was associated with poor prognostic features and independently associated with adnexal involvement [11–13], and patients with ovarian and lymph nodes metastasis presented with a higher mean initial serum Ca-125 [14,15]. Several studies support that status for estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) from preoperative endometrial biopsy in primary tumors are independent prognostic markers [16,17]. The loss of ER and PR status is associated with type II, higher tumor grade, and deep myometrial invasion, which were considered to be aggressive endometrial cancer. Young endometrial cancer patients need systematic clinical implementation studies of potentially useful clinic-pathologic characteristics.
On this background, we explored the rate of ovarian metastasis and analyzed the risk factors associated with ovarian metastasis in endometrial cancer patients in our center.
Material and Methods
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS:
Data analysis was performed with SPSS 19.0 statistical software. The categorical data were assessed using the chi-square test or exact probability test. Logistic regression analysis was applied to analyze the relationship of clinicopathological factors and ovarian metastasis. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and the area under the curve (AUC) were used to evaluate the diagnostic value of CA-125 in ovarian metastasis.
This study complied with the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital. The research ethics register number was SYSEC-KY-KS-2018-073. The data are anonymous, and the requirement for informed consent was therefore waived.
Results
A total of 565 patients with endometrial cancer were enrolled in the present study from January 2003 to October 2013. The median age of the study population was 53 years (range 17–78 years). There were 366 stage IA cases, 55 stage IB cases, 30 stage II cases, and 114 stage III, and stage IV cases. The clinical and pathological characteristics are presented in Table 1.
The overall incidence of ovarian metastasis was 5.7%. Among them, the incidence in patients with stage IIIC1 and IIIC2 was 7.7% and 16.7%, respectively. The correlations between the risk of ovary metastasis and age, myometrial invasion, tumor size, histological type, tubal involvement, lymph-vascular space invasion (LVSI), lymph node metastasis, cervical involvement, parametrial involvement, menopause, vaginal involvement, and positive peritoneal washings/ascites are displayed in Table 2. Logistic regression analysis suggested that deeper myometrial invasion, tubal involvement, and parametrial involvement were independent risk factors for ovarian metastasis in endometrial cancer (
A total of 458 patients underwent CA-125 serum testing, and the CA125 level of 144 patients was higher than 35 IU/L. When CA-125 was elevated, the incidence of ovarian metastasis was 15.2%, compared to 1.6% when CA-125 was normal (Table 3). In the group of patients with ovarian metastasis, the CA125 concentration was 372.24±704.99 IU/L. In the group of patients without ovarian metastasis, the CA125 concentration was 48.49±123.49 IU/L. We observed significantly higher CA125 concentrations (
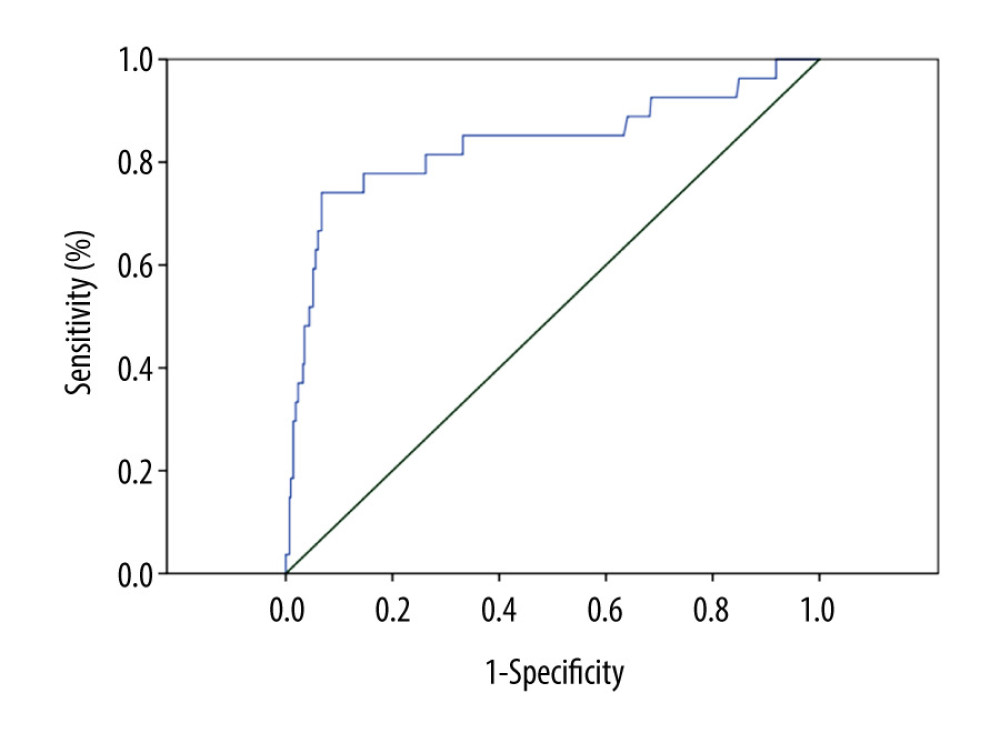
Based on the ROC curve analysis carried out in 458 patients, the cutoff point was determined for CA125 as above 110.5 IU/L (sensitivity 74.1%, specificity 93.7%; 95%CI: 0.726–0.900;
For further analysis, immunohistochemistry was used to examine ER and PR in a total of 504 patients. Ovarian metastasis was seen in 13% of 69 patient samples with loss of estrogen receptor (ER−) staining and in 12.2% of 49 patient samples with progesterone receptor loss (PR−). Univariate analysis revealed that loss of estrogen receptor (ER−) were associated with ovarian metastasis (
Of 253 patients with normal CA125 and positive ER, only 3 (1.19%) had ovarian metastasis, and the CA125 concentration was 17.62±7.55 IU/L. However, among the 25 patients with elevated CA125 and ER−, 6 (24.00%) had ovarian metastasis, a much greater incidence (Table 5).
Among the 32 patients with confirmed ovarian malignancy, 21 were younger than 50 years old. Of note, 24 cases occurred in patients with masses larger than 2 cm and 19 occurred in patients with more than 50% myometrial invasion. Nine patients had LVSI, 7 had lymph node metastasis, and 10 were ultimately found to have parametrial involvement.
Discussion
The menopausal transition usually begins in the middle to late 40s, with menopause occurring at a median age of 49.5 years in China. In the present study, 52.1% of patients with endometrial cancer were premenopausal, 30.5% were younger than 50 years, and 10.3% were younger than 40 years. These findings supported that among women who have been diagnosed with cancer in the uterus, there was a fairly large percentage of younger women. However, the present study did not find an association between younger age and clinicopathologic risk factors for ovarian metastasis.
Previously studies have reported that the incidence of metastatic ovarian cancer and coexisting malignancies in endometrial cancer varies from 5% to 29%, which may be due to sample size, cancer characteristics, ethnic group, and different pathological diagnostic criteria [5–10]. Lee et al. found that it is possible to preserve ovaries in young women with early-stage endometrial carcinoma with a thorough and extensive intraoperative exploration, and only 2 out of 206 (0.97%) patients without a visible extra-uterine lesion detected during surgery had ovarian cancer [6]. However, Walsh et al. retrospectively studied 102 patients younger than 45 years with endometrial cancer and found that 26 of 102 (25%) patients had coexisting epithelial ovarian cancers, 15% of patients (4/26) had preoperative diagnostic imaging of normal ovaries, and 15% of patients (4/26) had normal morphological appearance of the ovarian adnexa. Therefore, these researchers believed that patients with ovarian preservation are at high risk [5]. In the present study, patients with ovarian coexisting malignancies were excluded, and the incidence of ovarian metastasis in endometrial cancer was 5.7%, which is consistent with previous findings.
Multiple clinicopathological factors have been consistently demonstrated to predict ovarian metastasis [18–22]. Deep myometrial invasion in the excised uterus was the strongest predictive factor for ovarian metastasis, associated with a 66-fold increased risk of ovarian metastasis [18]. In the present study, univariate analysis and multivariate analysis revealed that deeper myometrial invasion, tubal involvement, and parametrial involvement were independent risk factors for ovarian metastasis. Currently, for the preoperative identification of ovarian metastasis, assessment of myometrial invasion and tumor involvement by images are recommended. However, in a preoperative setting, the assessment of deep myometrial invasion by MRI, CT, or transvaginal ultrasound has several challenges.
The wide use of CA-125 in the management of epithelial ovarian cancer, as a tumor marker for screening and monitoring, suggest the likelihood of a specific correlation between CA-125 and ovarian metastasis. Earlier studies showed that preoperative elevated CA-125 was also associated with poor prognostic features and was an independent prognosticator for poor outcome [11,12]. In our study, further analysis of CA125 level revealed that the incidence of ovarian metastasis was 15.2% when CA125 was elevated, compared to only 1.6% when CA-125 was normal. Multivariate analysis revealed that elevated CA125 level was associated with ovarian metastasis. Similar results were also observed in a retrospective study of 61 patients with uterine papillary serous carcinoma [13].
There have been calls for systematic clinical implementation studies of the cutoff values that may be useful for prediction of ovarian metastasis in endometrial cancer patients. Patients with ovarian and lymph nodes metastasis presented with a higher mean initial serum Ca-125; the mean (range) was 308.4 (5–1086) U/mL, the optimal cutoff value was 40.8 U/mL, and >70 U/mL were independent risk factor for poor progression-free and overall survival [14,15]. According to our data, in patients with ovarian metastasis, the CA125 concentration was 372.24±704.99 IU/L, a CA-125 level of 110.5 IU/L was the best cutoff for predicting ovarian metastasis. In addition, the accuracy of serum CA-125 levels for preoperative diagnostic was 74.1%. Thus, we recommend that the optimal cutoff value of serum CA-125 levels higher than the common value (0–35 U/ml) should be considered for young endometrial patients before undergoing initial treatment.
Low ER immunohistochemical staining was reported to be significantly correlated with an aggressive clinicopathologic phenotype and reduced survival in all endometrial cancer patient cohorts studied [23–26]. On the other hand, double-negative hormone receptor status in endometrial cancer preoperative curettage histology independently predicted lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in a prospective multicenter study [16]. Using hormone receptor status to improve risk-stratification for selecting patients unlikely to benefit from oophorectomy seems justified. In the present study, ovarian metastasis was high in patient samples with ER loss (13%) and PR loss (12.2%), and univariate analysis revealed that ER loss was associated with ovarian metastasis (
However, this study is limited owing to the relatively small sample size. The study was retrospective and performed in a single institution, which may have caused selection bias. Because ovarian metastasis is not common in Chinese patients (only 32 of 565 patients were identified), it was hard to determine the exact histopathological type of ovarian metastasis that affects CA-125 levels. Another limitation is that the data regarding recurrence in ovarian metastasis patients could not be analyzed. Subsequent studies should thoroughly investigate the relationship between recurrence and prognosis in this population.
Conclusions
The present study suggests that elevated serum CA-125 levels contribute to preoperative prediction, and patients with serum Ca-125 >110.5 U/mL could have higher potential risk. Use of estrogen receptor status may improve identification of patients at risk of ovarian metastasis. Preoperative workup should be complete to make an appropriate treatment plan, as ovarian metastasis can occur in women with abnormal CA-125 level, deeper myometrial invasion, tubal involvement, parametrial involvement, and who are ER-negative. Preoperative assessment of serum CA-125 level and hormone receptor status is easily performed, and these could be attractive methods to preoperatively identify high-risk patients.
Tables
Table 1. Patient, clinical, and pathological characteristics.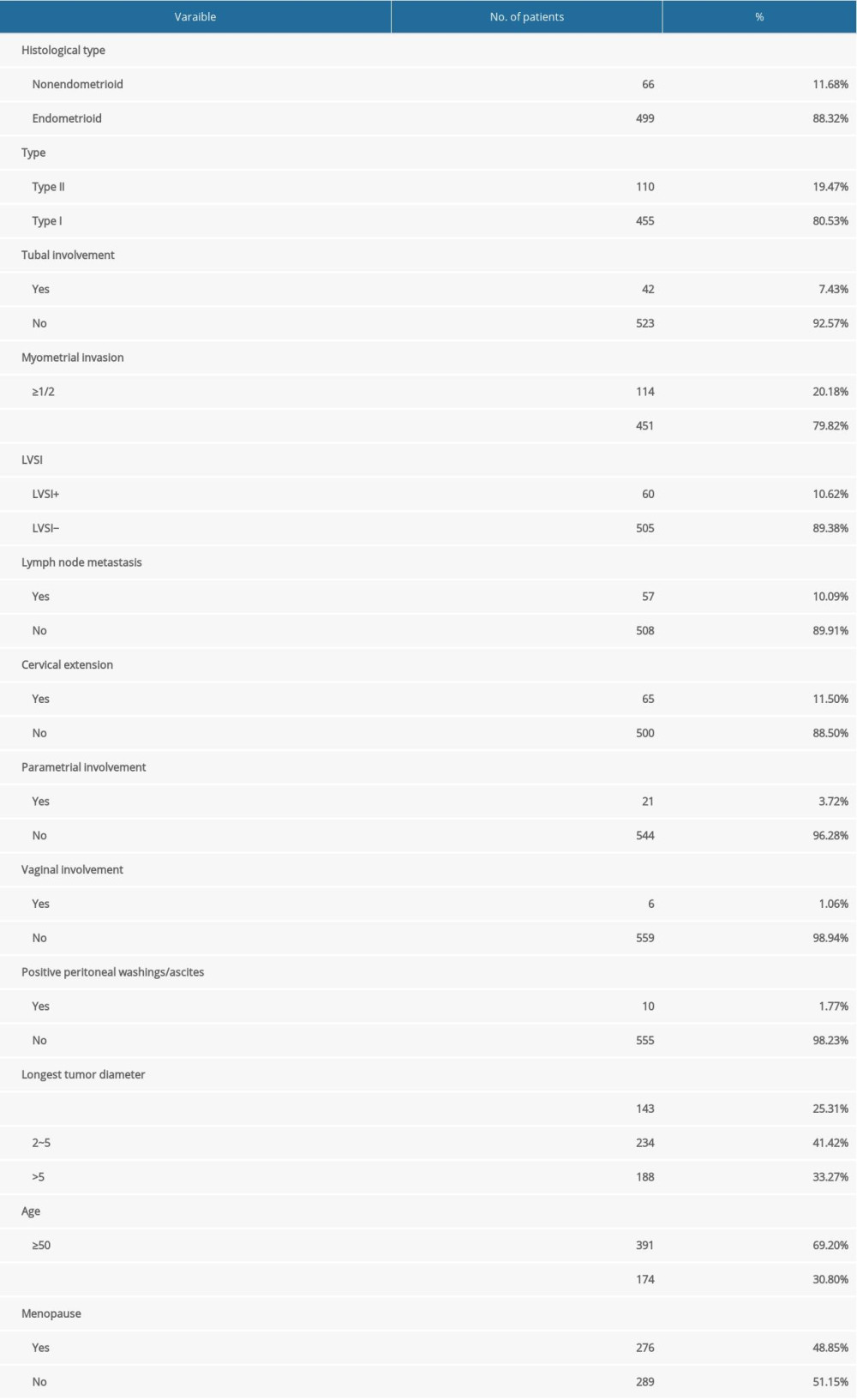 Table 2. Univariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis.
Table 2. Univariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis.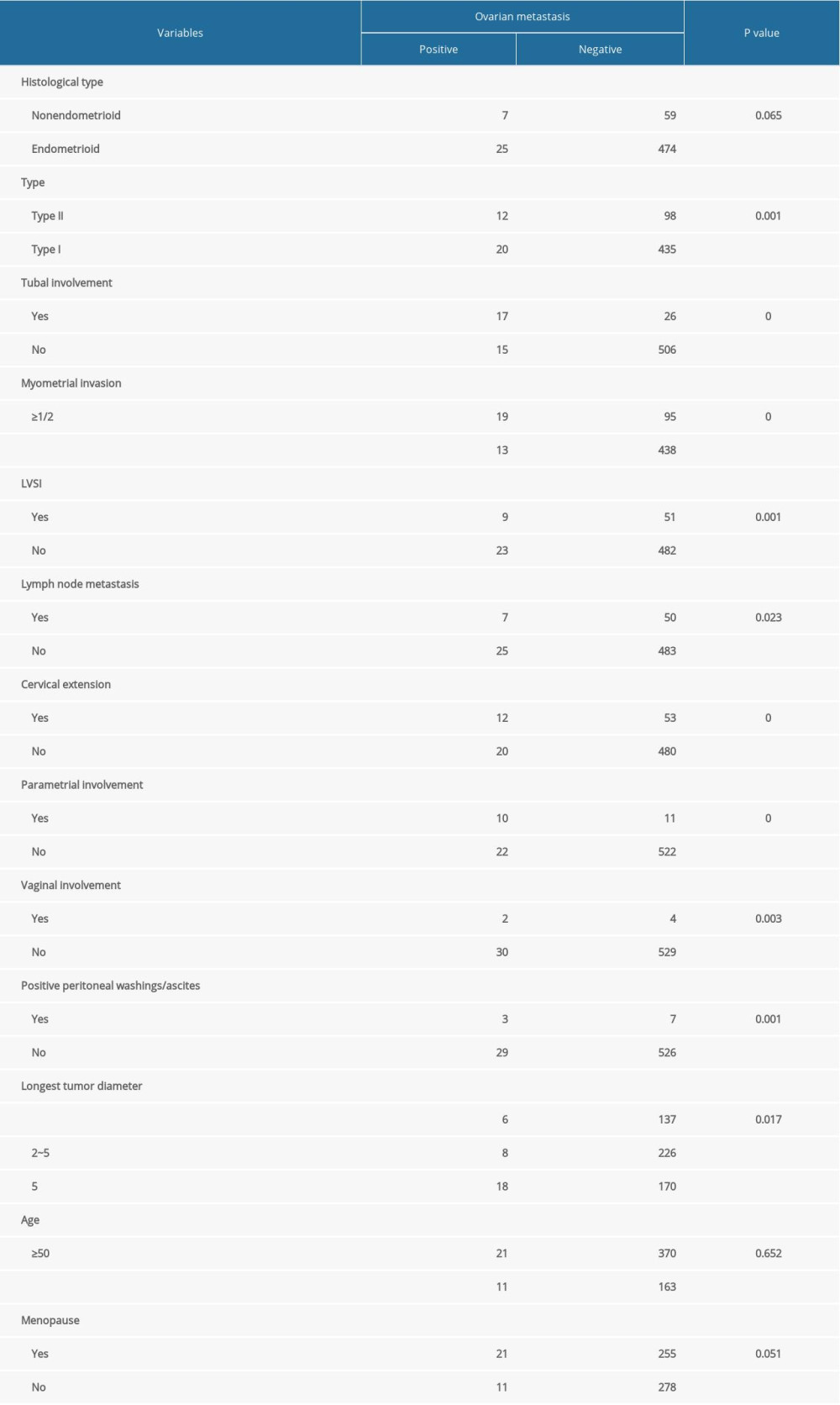 Table 3. CA125 level, ER, and PR of patients with endometrial cancer.
Table 3. CA125 level, ER, and PR of patients with endometrial cancer. Table 4. Multivariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis.
Table 4. Multivariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis.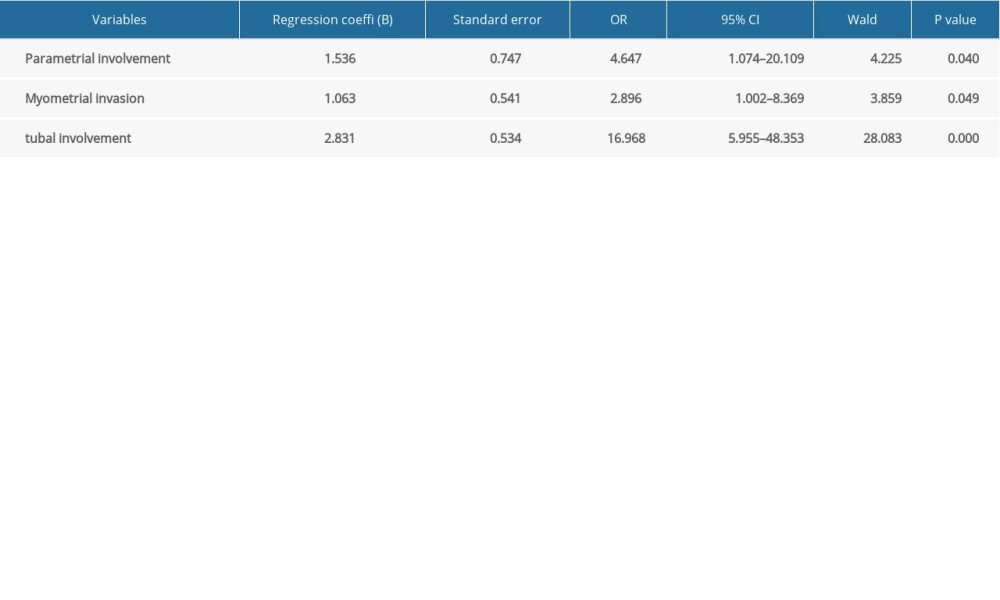 Table 5. Status for ER and CA125 level in patients with ovarian metastasis.
Table 5. Status for ER and CA125 level in patients with ovarian metastasis.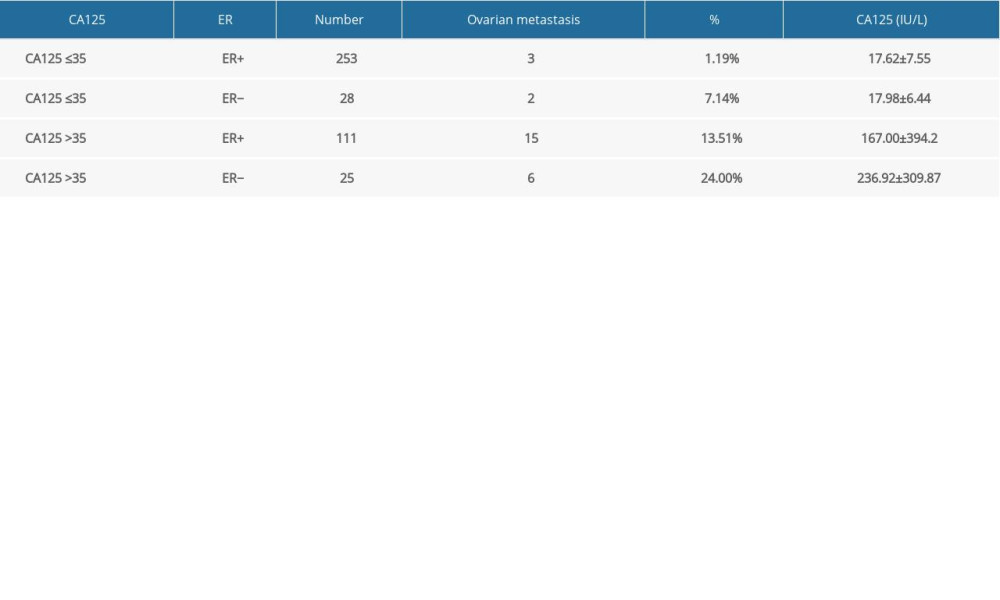
References
1. National Comprehensive Cancer Center (NCCN): NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: Uterine neoplasms, 2021 Version 1
2. Atsma F, Bartelink ML, Grobbee DE, Postmenopausal status and early menopause as independent risk factors for cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis: Menopause, 2006; 13; 265-79
3. Rocca WA, Grossardt BR, de Andrade M, Survival patterns after oophorectomy in premenopausal women: A population-based cohort study: Lancet Oncol, 2006; 7; 821-28
4. Wright JD, Buck AM, Shah M, Safety of ovarian preservation in premenopausal women with endometrial cancer: J Clin Oncol, 2009; 27(8); 1214-19
5. Walsh C, Holschneider C, Hoang Y, Coexisting ovarian malignancy in young women with endometrial cancer: Obstet Gynecol, 2005; 106(4); 693-99
6. Lee TS, Jung JY, Kim JW, Feasibility of ovarian preservation in patients with early-stage endometrial carcinoma: Gynecol Oncol, 2007; 104(1); 52-57
7. Baiocchi G, Clemente AG, Mantoan H, Adnexal involvement in endometrial cancer: Prognostic factors and implications for ovarian preservation: Ann Surg Oncol, 2020; 27(8); 2822-26
8. Reijnen C, Küsters-Vandevelde HVN, Ligtenberg MJL, Molecular profiling identifies synchronous endometrial and ovarian cancers as metastatic endometrial cancer with favorable clinical outcome: Int J Cancer, 2020; 147(2); 478-89
9. Li M, Wu S, Xie Y, Cervical invasion, lymphovascular space invasion, and ovarian metastasis as predictors of lymph node metastasis and poor outcome on stages I to III endometrial cancers: A single-center retrospective study: World J Surg Oncol, 2019; 17(1); 193
10. Wang T, Zhang X, Lu Z, Comparison and analysis of the clinicopathological features of SCEO and ECOM: J Ovarian Res, 2019; 12(1); 10
11. Reijnen C, Visser NC, Kasius JC, Improved preoperative risk stratification with CA-125 in low-grade endometrial cancer: A multicenter prospective cohort study: J Gynecol Oncol, 2019; 30(5); e70
12. Kotowicz B, Fuksiewicz M, Jonska-Gmyrek J, Preoperative serum levels of YKL 40 and CA125 as prognostic indicators in patients with endometrial cancer: Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 2017; 215; 141-47
13. Schmidt M, Segev Y, Sadeh R, Cancer antigen 125 levels are significantly associated with prognostic parameters in uterine papillary serous carcinoma: Int J Gynecol Cancer, 2018; 28(7); 1311-17
14. Broeders FM, van der Wurff AA, Pijnenborg JM, Preoperative identification of synchronous ovarian and endometrial cancers: The importance of appropriate workup: Int J Gynecol Cancer, 2012; 22(8); 1325-31
15. Kim HS, Park CY, Lee JM, Evaluation of serum CA-125 levels for preoperative counseling in endometrioid endometrial cancer: A multi-center study: Gynecol Oncol, 2010; 118; 283-88
16. Trovik J, Wik E, Werner HM, Hormone receptor loss in endometrial carcinoma curettage predicts lymph node metastasis and poor outcome in prospective multicentre trial: Eur J Cancer, 2013; 49(16); 3431-41
17. Salvesen HB, Haldorsen IS, Trovik J, Markers for individualized therapy in endometrial carcinoma: Lancet Oncol, 2012; 13(8); e353-61
18. Ignatov T, Eggemann H, Burger E, Ovarian metastasis in patients with endometrial cancer: Risk factors and impact on survival: J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2018; 144(6); 1103-7
19. Li J, Zhu Q, Yang B, Risk factors for ovarian involvement in young and premenopausal endometrioid endometrial cancer patients: Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 2018; 222; 151-54
20. Kinjyo Y, Kudaka W, Ooyama T, Ovarian preservation in young women with endometrial cancer of endometrioid histology: Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand, 2015; 94(4); 430-34
21. Pan Z, Wang X, Zhang X, Retrospective analysis on coexisting ovarian cancer in 976 patients with clinical stage I endometrial carcinoma: Gynecol Oncol, 2009; 114; 99-104
22. Lin KY, Miller DS, Bailey AA, Ovarian involvement in endometrioid adenocarcinoma of uterus: Gynecol Oncol, 2015; 138(3); 532-35
23. Wik E, Ræder MB, Krakstad C, Lack of estrogen receptor-α is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and PI3K alterations in endometrial carcinoma: Clin Cancer Res, 2013; 19(5); 1094-105
24. Salama A, Arafa M, El Zahaf E, Potential role for a panel of immunohistochemical markers in the management of endometrial carcinoma: J Pathol Transl Med, 2019; 53(3); 164-72
25. Wang C, Tran DA, Fu MZ, Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 receptor markers in endometrial cancer: J Cancer, 2020; 11(7); 1693-701
26. Porzio R, Cordini C, Rodolfi AM, Triple-negative endometrial cancer: Incidence and prognosis in a monoinstitutional series of 220 patients: Oncol Lett, 2020; 19(3); 2522-26
Tables
 Table 1. Patient, clinical, and pathological characteristics.
Table 1. Patient, clinical, and pathological characteristics. Table 2. Univariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis.
Table 2. Univariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis. Table 3. CA125 level, ER, and PR of patients with endometrial cancer.
Table 3. CA125 level, ER, and PR of patients with endometrial cancer. Table 4. Multivariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis.
Table 4. Multivariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis. Table 5. Status for ER and CA125 level in patients with ovarian metastasis.
Table 5. Status for ER and CA125 level in patients with ovarian metastasis. Table 1. Patient, clinical, and pathological characteristics.
Table 1. Patient, clinical, and pathological characteristics. Table 2. Univariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis.
Table 2. Univariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis. Table 3. CA125 level, ER, and PR of patients with endometrial cancer.
Table 3. CA125 level, ER, and PR of patients with endometrial cancer. Table 4. Multivariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis.
Table 4. Multivariate analyses of clinical pathological risk factors for ovarian metastasis. Table 5. Status for ER and CA125 level in patients with ovarian metastasis.
Table 5. Status for ER and CA125 level in patients with ovarian metastasis. In Press
15 Apr 2024 : Laboratory Research
The Role of Copper-Induced M2 Macrophage Polarization in Protecting Cartilage Matrix in OsteoarthritisMed Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943738
07 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Knowledge of and Attitudes Toward Clinical Trials: A Questionnaire-Based Study of 179 Male Third- and Fourt...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943468
08 Mar 2024 : Animal Research
Modification of Experimental Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) in Rat Pups by Single Exposure to Hyp...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943443
18 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Comparative Analysis of Open and Closed Sphincterotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Anal Fissure: Safety an...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.944127
Most Viewed Current Articles
17 Jan 2024 : Review article
Vaccination Guidelines for Pregnant Women: Addressing COVID-19 and the Omicron VariantDOI :10.12659/MSM.942799
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942799
14 Dec 2022 : Clinical Research
Prevalence and Variability of Allergen-Specific Immunoglobulin E in Patients with Elevated Tryptase LevelsDOI :10.12659/MSM.937990
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e937990
16 May 2023 : Clinical Research
Electrophysiological Testing for an Auditory Processing Disorder and Reading Performance in 54 School Stude...DOI :10.12659/MSM.940387
Med Sci Monit 2023; 29:e940387
01 Jan 2022 : Editorial
Editorial: Current Status of Oral Antiviral Drug Treatments for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Non-Hospitalized Pa...DOI :10.12659/MSM.935952
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e935952