29 October 2020: Clinical Research
Influence of Scapula Training Exercises on Shoulder Joint Function After Surgery for Rotator Cuff Injury
Ming Zhang12ABDEG*, Jingjie Zhou12BEF, Yuming Zhang12CDF, Xiufang Zhang12BDF, Jie Chen12BDE, Wei Chen12AEFDOI: 10.12659/MSM.925758
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e925758
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The aim of this study was to assess the clinical effectiveness of scapula training exercises on shoulder function after surgery for rotator cuff injury.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: Forty-six patients with rotator cuff injury after surgery were randomized into the experiment group or control group. Both groups were treated with conventional therapeutic exercise and physical therapy, and scapular training exercise was added to the experiment group. Patient status was evaluated by Constant-Murley scale (CMS), visual analogue scale (VAS), and the active range of motion (ROM) of the shoulder before and after 6 weeks and 12 weeks of treatment.
RESULTS: After 6 weeks and 12 weeks of treatment, all evaluations of the 2 groups were significantly improved as compared with those before treatment (P<0.05). Moreover after 6 weeks of treatment, the CMS (pain, daily life, range of activity, total scores), VAS and ROM (anteflexion) in the experimental group were significantly better than those in the control group (P<0.05). However, there was no significant difference in CMS (strength test) and ROM (abduction, rear extension) (P>0.05). After 12 weeks of treatment, all items in the experimental group were significantly improved compared to the control group (P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS: The combination of conventional rehabilitation interventions and scapular training exercise were an effective treatment of the shoulder dysfunction. Moreover, increased Scapula training exercise had better effect on the improvement of shoulder function.
Keywords: Exercise, rotator cuff, Shoulder Joint, Exercise Therapy, Range of Motion, Articular, Rotator Cuff Injuries, Scapula, Shoulder
Background
The shoulder plays an extremely important role in daily life and is the joint with the greatest motion range and flexibility in humans. Shoulders are easily injured by external forces. Rotator cuff injury is one of the most common shoulder injuries. For shoulder dysfunction resulting from rotator cuff injury (RCI), traditional rehabilitation therapy is often applied to the specific shoulder joint, called the glenohumeral joint. The overall condition of the shoulder joint is seldom considered, so it is difficult for therapists to achieve the best curative effect in daily treatments. There have been few reports on scapula training exercise for shoulder joint rehabilitation therapy in China. Internationally, there have been several handbooks published on scapula training exercise for patients with shoulder joint injury, such as the USA’s HSS (Hospital for Special Surgery), which emphasized the role of scapula motions in shoulder function [1]. Medical technology has been developed for minimally invasive shoulder joint surgery, and rotator cuff injury prostheses help patients return to work, thus relieving the economic and social pressures, and early rehabilitation therapy is beneficial [2]. New therapeutic techniques such as radial shockwave therapy also promoted the functional recovery of patients with RCI [3]. In the present study, we compared the effects of normal rehabilitation therapy and additional scapular therapeutic exercise in patients with dysfunction caused by RCI.
Material and Methods
CLINICAL OBSERVATION:
We enrolled 46 patients who were admitted to Xuzhou Rehabilitation Hospital and diagnosed with RCI from June 2016 to June 2018. The study was approved by the Institutional Medical Ethics Committee of Xuzhou Rehabilitation Hospital (No. 20160601001). The inclusion criteria were: (1) patients diagnosed with RCI by MRI with clinical signs after shoulder dysfunction resulting from external injury; (2) the degree of RCI could be divided into partial-thickness injury and full-thickness injury; and (3) the patients had received arthroscopic repair of RCI and repair of small-incision RCI.
The exclusion criteria were: (1) previous scapula dysfunction; (2) shoulder joint activity disorders resulting from central nerve injury or peripheral nerve injury; (3) external injury combined with upper-limb fracture; and (4) other diseases and were not suitable for rehabilitation therapy.
After providing signed informed consent, patients were randomly divided into the experiment group and the control group using a random number table, and there was no statistically significant difference between the 2 groups in sex, age, disease course, and other general information (P>0.05). The relevant data are shown in Table 1.
THERAPEUTIC METHOD:
Patients in both groups were treated with a rehabilitation program implemented after conventional RCI repair, including the conventional therapeutic exercise and physical therapy, and the scapula training exercise was specifically added to the experiment group. The study profile is shown in Figure 1.
The gymnastics bars continued to be used for shoulder joint anteflexion exercise, outreach, and internal and external rotation, and the patients also used shoulder pulley, shoulder ladder, and shoulder joint rotation training equipment to assist training as long as it did not cause shoulder joint pain [6]. If patients had obvious joint disorders, joint mobilization was first performed to distract the articular surface [7] by grade II massage with the glenohumeral joint in resting position. If the pain worsened, the massage was reduced to grade I massage. If patients had no discomfort and extra joint movement was carried out, the massage was increased to grade III–IV massage, and the training was performed once every other day or once a day, and the training time was 15–20 minutes each time.
Scapula training exercise: Patients performed training of range of scapula motion 2 weeks after the operation, and the passive activity training of the scapula was first conducted on the surface of scapula. If scapula motion was obviously restricted, the patients held the arm in a neutral lateral position with the help of a pillow, and the physiotherapist placed one hand on the shoulder joint places the other hand in the inferior angle of the scapula to assist in exercise of elevation, subsidence, protraction, rear protraction of the scapula in the walls of the chest in the pain-free range. At the same time, the mild scapula separation and drawing exercise was added to improve scapula flexibility, and then the patients performed scapula adduction and outreach activity training with scapula plane in supine position, as well as the resistance training by corresponding massages after the activity of patients was improved. If possible, the patients performed the above-mentioned training gradually in sitting position. The patients started strength training of muscles around the scapula 4 weeks after the operation. The massage resistance training was first added to the range of motion training, and anterior drawer and rear protraction resistance training was carried out with the help of physicians to assist strength training of the serratus anterior muscle. If possible, the patients increased the rotator cuff muscle strength by internal and external rotation with the help of an elastic strap while standing. The scapula stability training was added to the training of motion range and muscle strength 6 weeks after the operation, and the dynamic closed-chain training could be selected. For instance, the yoga ball stability training could be carried out with the table leaning at an angle of 45°, and the yoga ball was first pushed down to support weight upon 60° anteflexion of both shoulders, and the angle of the treatment table was gradually changed until the anteflexion degree of both shoulders reached 90°, and then the patients could support their weight with only one arm [9]. The above-mentioned scapula training exercise should be performed once a day or once every other day according to the condition of the patient. The course of the above-mentioned treatment lasted for 3 months.
EVALUATION CRITERIA:
The evaluation and comparison of patients in both groups before treatment and at 6 and 12 weeks after the operation were carried out using the Constant-Murley shoulder joint function scale (CMS), visual analogue scale (visual analogue scale, VAS), and the range of shoulder joint anteflexion, backward extension, and active outreach movement, respectively.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS:
IBM SPSS19.0 statistical software was used to carry out statistical analysis. Enumeration data were assessed using the chi-square test. Quantitative data are expressed as mean standard deviation (χ̄±
Results
INTRA-GROUP COMPARISON OF EXPERIMENTAL GROUP AND CONTROL GROUP:
After 6 and 12 weeks of treatment, CMS (pain, daily activity, range of activity, strength test, total scores), VAS score, and shoulder ROM (flexion, abduction, rear extension) in both groups were significantly improved as compared with those before treatment, and the difference had statistical significance (P<0.05). After 12 weeks of treatment, the CMS (daily life, range of activities, total scores) was significantly improved compared with 6 weeks later (P<0.05). CMS (pain and strength test) was improved compared with that after 6 weeks, and the difference has statistical significance (P<0.05). After 6 and 12 weeks of treatment, the VAS score and the ROM of shoulder joint (anteflexion, abduction, rear extension) were significantly improved as compared with those before treatment (P<0.05), and the effect after 12 weeks treatment was better than that after 6 weeks treatment (P<0.05). The corresponding results are shown in Tables 2 and 3.
COMPARISON BETWEEN EXPERIMENTAL GROUP AND CONTROL GROUP:
There was no significant difference in CMS (pain, daily activity, range of activity, strength test, total score), VAS score, and shoulder ROM (anteflexion, abduction, rear extension) between the 2 groups before treatment (P>0.05). After 6 weeks of treatment, the CMS (pain, daily life, range of activity, total scores), VAS score, and shoulder range of motion (anteflexion) in the experimental group were significantly better than those in the control group (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in CMS (strength test) and shoulder ROM (abduction, rear extension) (P>0.05). After 12 weeks of treatment, the CMS (pain, daily life, range of activity, strength test, total scores), VAS score, and shoulder range of motion (anteflexion, abduction, rear extension) in the experimental group were significantly better than those in the control group, and the difference had statistical significance (P<0.05). The corresponding results were shown in Tables 2 and 3.
Discussion
The rotator cuff is composed of supraspinatus muscle, infraspinatus muscle, teres minor, and tendon of subscapularis muscle and it is attached to the large and small nodules of the proximal humerus in the shape of a sleeve, which increases the stability of the glenohumeral joint. In addition, the rotator cuff also plays an important role in stability and function of the shoulder joint. The passive tension of the rotator cuff can cause extrusion stress on the surface of the glenohumeral joint. Because the concavity-compression mechanism provides stability for the shoulder joint, the synchronous and active contraction of rotator cuff muscles in the process of movement keep the position between the joint surface relatively constant. RCI is the most common shoulder joint degenerative disease. In addition, patients with RCI account for 17–41% of the population, which leads to a higher possibility of disability [13]. The scapulothoracic joint has no real joint anatomy, but the combination of the bones and the location of scapula in the chest wall provides the foundation for movement of the glenohumeral joint, which plays a significant role in the recovery of shoulder joint function of patients with RCI. The main objective of the present study was to assess the functional recovery of patients with shoulder joint disorders resulting from rotator cuff injury [14]. Usually, rehabilitation only focusses on the shoulder joint itself and neglects the important role of the scapula in shoulder joint disorders, and joint mobilization can only deal with the glenohumeral joint itself. Therefore, we explored whether scapula movement, strength training of muscles around the scapula, and stability training of the scapula significantly alleviate shoulder pain resulting from RCI and improve shoulder joint disorders.
The movement and position of the scapula play an important role in shoulder joint function. Solem-Bertoft and many other scholars [15] evaluated patients in sitting position and the position of the scapula before the patients were treated by physicians. For instance, the forward posture of the scapula might be aggravated in the forward posture of the chest, head, and neck resulting from pain, and the posture might worsen infrascapular stenosis and infrascapular rotator cuff tendinopathy, thus resulting in aggravation of pain. Ludewig and many other scholars made an analysis of the motion coordination system of healthy people’s scapulas as well as the forward spin and downward spin of the scapula in 2009 [16] and 2010 [17], which indicated that the normal movement and correct position of the scapula play an important role in shoulder joint function. The results of this research also indicated that shoulder ROM in the experimental group after 12 weeks of treatment was significantly improved compared to the control group (
Liu Xiaohua and many other scholars [18] suggested applying isometric strength training to patients treated with calcific rotator cuff tendinitis after shoulder injury surgery 2 weeks after the operation, and to apply resistance training 6 weeks after the operation, as long as the strength training does not aggravate the shoulder pain. Escamilla [19], Horsley [20], and many other scholars put advocated scapulohumeral muscle strength training, especially training of rotator cuff muscles, which help improve glenohumeral joint stability, expanding shoulder ROM, and improving the curative effect of patients with scapula glenoid labrum tear.
Tsuruike and many other scholars [21] showed that long-term shoulder immobilization can lead to serratus anterior muscle fatigue, which reduces the rotation degree and extension degree of the scapula and leads to forward lead and up-lifting of the humerus head, thus resulting in secondary acromion impact injury and rotator cuff tears. In addition, the muscle group in the middle and lower part of the serratus anterior muscle keep the normal lacuna of the subacromial joint upon outreach of the humerus, which helps shoulder joint outreach, so it was necessary for patients to receive rehabilitation training to repair the muscles around the scapular after shoulder joint immobilization, especially the serratus anterior muscle. The patients in the experimental group of this research were treated with strength training of muscles around the scapula and performed closed-chain stability training based on the normal rehabilitation therapy. We found that the patients in the experimental group had better results than patients in the control group in terms of shoulder joint pain, daily activity, and strength test, and the differences were statistically significant (
In the assessments carried out 6 weeks after postoperative rehabilitation treatment, there was no significance difference between the 2 groups in terms of strength test and ROM of shoulder abduction and extension in CMS score (
In conclusion, physiotherapists need to first analyze the main causes of shoulder joint disorders in the later rehabilitation and treatment process, and then need to formulate a targeted rehabilitation and treatment schedule according to the cause of disease. However, scapula movement was neglected by most of our physicians in the daily rehabilitation and treatment; thus, the curative effect of rehabilitation and treatment was not obvious, so physiotherapists were required to first analyze scapula movement to formulate a rehabilitation and treatment schedule for patients with shoulder joint disorders. Especially for patients with early shoulder injury, the position and movement of scapula played an important role in shoulder joint function, and scapula movement in the early period, as well as expansion of range of scapula movement, have an important effect on the range of shoulder joint movement. The results of the present study show that physiotherapists need to pay more attention to scapula exercise training in treatment of patients after RCI surgery to assure the maximum efficacy of rehabilitation and treatment.
Conclusions
The combination of standard rehabilitation interventions and scapula training exercises are an effective treatment of shoulder joint dysfunction after rotator cuff injury repair. However, increasing scapula training exercises has obvious advantages in improving the pain outcomes, scope of activities, and total scores of functional assessments.
Figures
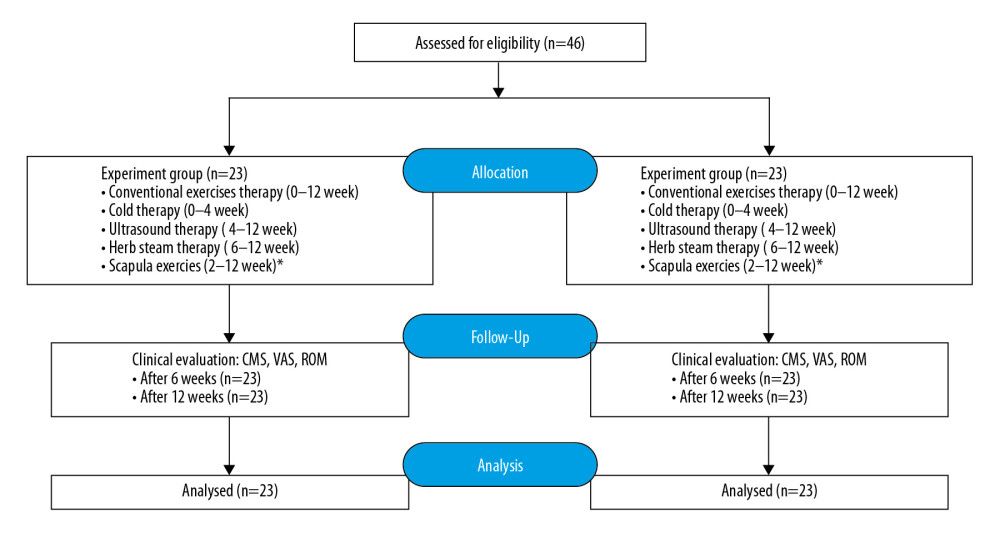 Figure 1. Study profile.
Figure 1. Study profile. References
1. Cioppa-Mosca J: Postsurgical rehabilitation guidelines for the orthopedic clinician, 2009; 484-96, Tianjin, Tianjin Science and Technology Translation Publishing House
2. Mather RC, Koenig L, Acevedo D, The societal and economic value of rotator cuff repair: J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2013; 95; 1993-2000
3. Dedes V, Tzirogiannis K, Polikandrioti M, Radial extracorporeal shockwave therapy versus ultrasound therapy in the treatment of rotator cuff tendinopathy: Folia Med (Plovdiv), 2019; 61(4); 612-19
4. van der Meijden OA, Paul Westgard P, Rehabilitation after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: Current concepts review and evidence-based guidelines: Int J Sports Phys Ther, 2012; 7; 197-218
5. Jeanfavre M, Husted S, Leff G, Exercise therapy in the non-operative treatment of full-thickness rotator cuff tears: A systematic review: Int J Sports Phys Ther, 2018; 13(3); 335-78
6. Donatelli RA: Physical therapy of the shoulder, 2011; 62-67, Las Vegas, Elsevier
7. Wan L, Bian RInterventional effect of sustained translatory intra-articular mobilization technique on shoulder joint dysfunction following rotator cuff injury: Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2013; 28; 1021-23 [in Chinese]
8. Zhao CF, Peng DS, Rang MThe traditional Chinese medicine combined with Joint manipulation treatment of frozen shoulder: Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation, 2012; 27; 291-92 [in Chinese]
9. Zhang M, Zhou JJ, Zhang YM, Clinical effectiveness of scapulothoracic joint control training exercises on shoulder joint dysfunction: Cell Biochem Biophys, 2015; 72; 83-87
10. Ge YS, Chen SYShoulder function scoring system: Status quo and prospects: Chinese Journal of Orthopaedics, 2007; 27; 786-89 [in Chinese]
11. Boonstra AM, Schiphorst Preuper HR, Reneman MF, Reliability and validity of the visual analogue scale for disability in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain: Int J Rehabil Res, 2008; 31; 165-69
12. Wang YL: Rehabilitation evaluation and functional assessment, 2008; 133-35, Beijing, People’s Medical Publishing House
13. Wu H, Gu XD, Chen YCEffectiveness of comprehensive rehabilitations on shoulder motor function in elderly patients with rotator cuff injury]: Chinese Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 2010; 32; 660-61 [in Chinese]
14. Littlewood C, Bateman M, Clark D, Rehabilitation following rotator cuff repair: A systematic review: Shoulder Elbow, 2015; 7; 115-24
15. Solem-Bertoft EI, Thuomas KA, Westerberg CE, The influence of scapular retraction and protraction on the width of the subacromial space. An MRI study: Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993; 296; 99-103
16. Ludewig PM, Phadke V, Braman JP, Motion of the shoulder complex during multiplanar humeral elevation: J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2009; 91; 378-89
17. Ludewig PM, Hassett DR, Laprade RF, Comparison of scapular local coordinate systems: Clin Biomech, 2010; 25; 415-21
18. Liu XH, Guo XF, Yu JInfluence of systematic rehabilitation on the post-operative efficacy of surgery for calcified supraspinatus tendinitis: Chinese Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 2010; 32; 542-44
19. Escamilla RF, Yamashiro K, Paulos L, Shoulder muscle activity and function in common shoulder rehabilitation exercises: Sports Med, 2009; 39; 663-85
20. Horsley IG, Herrington LC, Rolf C, Does a SLAP lesion affect shoulder muscle recruitment as measured by EMG activity during a rugby tackle?: J Orthop Surg Res, 2010; 25; 5-12
21. Tsuruike M, Ellenbecker T, Serratus anterior and lower trapezius muscle activities during multi-joint isotonic scapular exercises and isometric contractions: J Athl Train, 2015; 50; 199-210
Figures
Tables
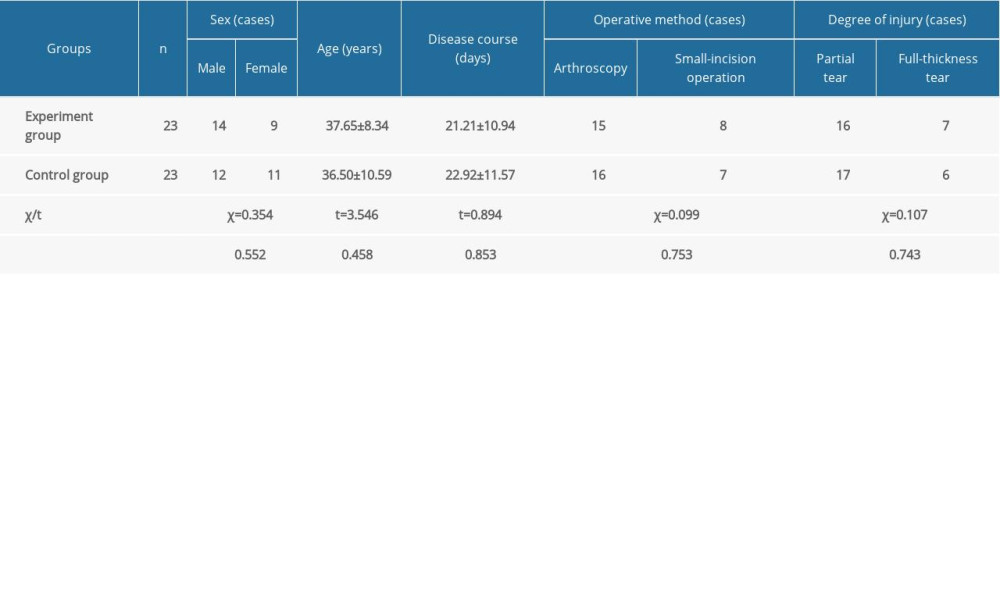 Table 1. General information of patients in the 2 groups (χ̄±s).
Table 1. General information of patients in the 2 groups (χ̄±s).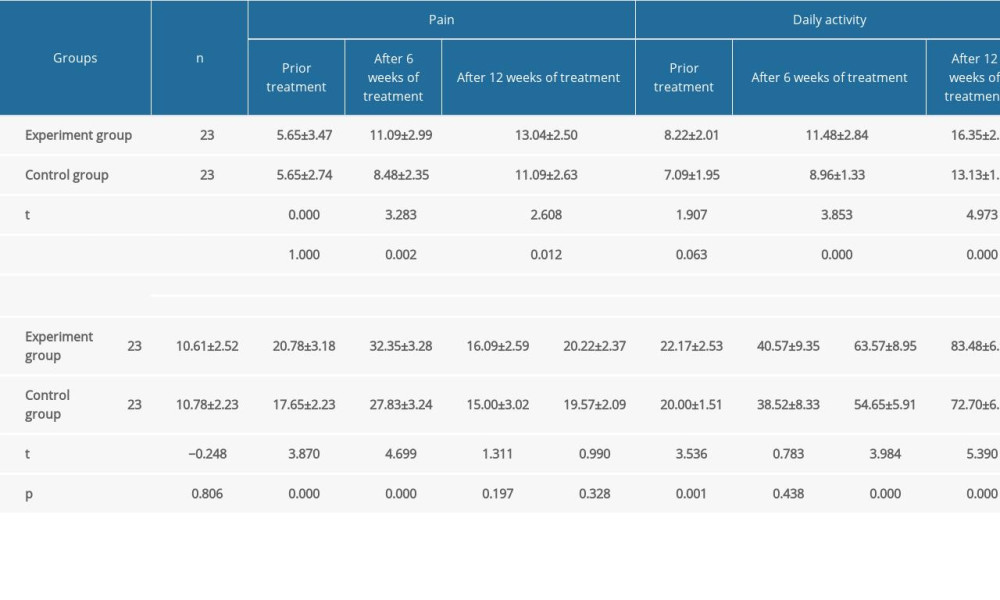 Table 2. Comparison of CMS scores between the 2 groups before and after treatment (scores, χ̄±s).
Table 2. Comparison of CMS scores between the 2 groups before and after treatment (scores, χ̄±s).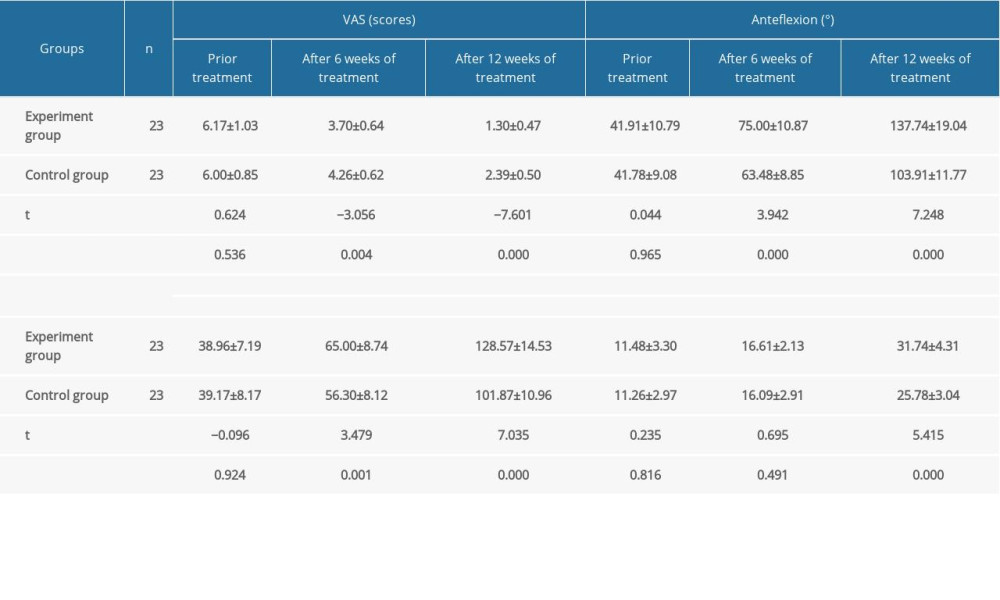 Table 3. Comparison of VAS score and shoulder joint ROM score between the 2 groups before and after treatment (χ̄±s).
Table 3. Comparison of VAS score and shoulder joint ROM score between the 2 groups before and after treatment (χ̄±s). Table 1. General information of patients in the 2 groups (χ̄±s).
Table 1. General information of patients in the 2 groups (χ̄±s). Table 2. Comparison of CMS scores between the 2 groups before and after treatment (scores, χ̄±s).
Table 2. Comparison of CMS scores between the 2 groups before and after treatment (scores, χ̄±s). Table 3. Comparison of VAS score and shoulder joint ROM score between the 2 groups before and after treatment (χ̄±s).
Table 3. Comparison of VAS score and shoulder joint ROM score between the 2 groups before and after treatment (χ̄±s). In Press
05 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Role of Critical Shoulder Angle in Degenerative Type Rotator Cuff Tears: A Turkish Cohort StudyMed Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943703
06 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Comparison of Outcomes between Single-Level and Double-Level Corpectomy in Thoracolumbar Reconstruction: A ...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943797
21 Mar 2024 : Meta-Analysis
Economic Evaluation of COVID-19 Screening Tests and Surveillance Strategies in Low-Income, Middle-Income, a...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943863
10 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Predicting Acute Cardiovascular Complications in COVID-19: Insights from a Specialized Cardiac Referral Dep...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942612
Most Viewed Current Articles
17 Jan 2024 : Review article
Vaccination Guidelines for Pregnant Women: Addressing COVID-19 and the Omicron VariantDOI :10.12659/MSM.942799
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942799
14 Dec 2022 : Clinical Research
Prevalence and Variability of Allergen-Specific Immunoglobulin E in Patients with Elevated Tryptase LevelsDOI :10.12659/MSM.937990
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e937990
16 May 2023 : Clinical Research
Electrophysiological Testing for an Auditory Processing Disorder and Reading Performance in 54 School Stude...DOI :10.12659/MSM.940387
Med Sci Monit 2023; 29:e940387
01 Jan 2022 : Editorial
Editorial: Current Status of Oral Antiviral Drug Treatments for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Non-Hospitalized Pa...DOI :10.12659/MSM.935952
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e935952








