06 December 2021: Database Analysis
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of 103 Patients with Rectal Adenocarcinoma Identifies the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient as an Imaging Marker for Tumor Invasion and Regional Lymph Node Involvement
Jaromir Kargol 1ABCDEF* , Wojciech Rudnicki 2CDE , Jakub Kenig 3DF , Justyna Filipowska 4BE , Ewa Kaznowska 5BE , Tomasz Kluz 6BE , Wiesław Guz 4BE , Elżbieta Łuczyńska 4ACDEFDOI: 10.12659/MSM.934941
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e934941
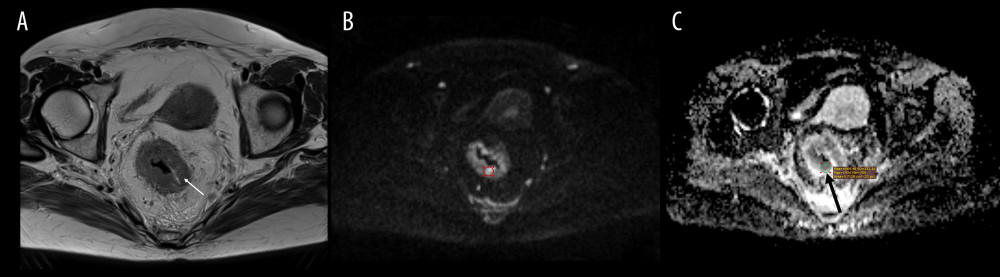
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance (MRI) scans in a 63-year-old woman with rectal cancer. A thickened rectal wall on (A) axial MRI T2-weighted image (arrow). High signal on (B) diffusion weighted image b=1000 s/mm2, and (C) low signal on corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map indicates the presence water diffusion restriction, the feature of malignancy. The visually determined brightest region within the tumor on (B) axial b=1000 s/mm2 image (the circle) and (C) the reading of minimum ADC value on corresponding ADC map in the region of interest (ROI) (black arrow). Medixant, RadiAnt DICOM Viewer (version 2020.2.3).


