25 October 2021: Database Analysis
RNA N6-Methyladenosine Patterns in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Reveal a Distinct Immune Infiltration Landscape and Clinical Significance
Hua Zhao 1CEFG , Qiujun Zhou 2BDEF , Chengwei Shi 2CD , Yaojian Shao 2CD , Junjie Ni 2CD , Jianying Lou 3ACE* , Shenyu Wei 2ACEF*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.930994
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e930994
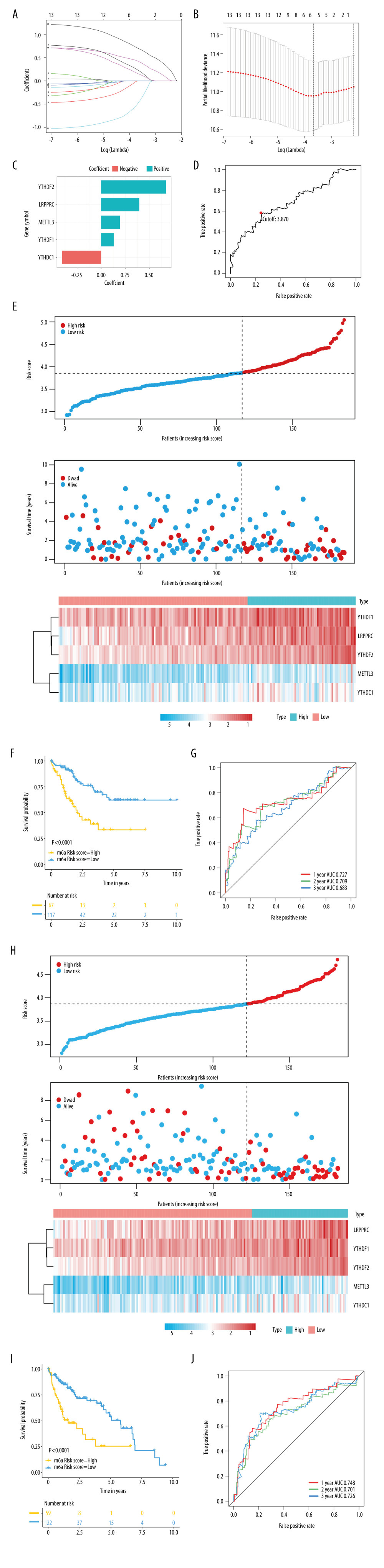
Figure 5 Establishment and validation of the prognostic panel using 5 N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modulators in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) cohort. (A, B) The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) Cox regression model identified 5 core prognostic m6A modulators in the TCGA training set. (C) The corresponding regression coefficients: YTHDF2, 0.6744; YTHDF1, 0.1318; YTHDC1, −0.4059; METTL3, 0.1954; and LRPPRC: 0.3962. (D) The optimal cutoff point (3.870) could distinguish patients with high and low risk. (E) Risk score distribution and survival overview for patients in the TCGA training set. (F) Prognostic analysis showed that the overall survival of patients was significantly lower in the high-risk score group than the low-risk score group in the TCGA training set. (G) Receiver operating characteristic curve was used to assess the predictive performance of m6A risk score. (H–J) The predictive performance of the m6A risk score was validated in the TCGA testing. R (version 3.6.1) software was used to create the pictures.


