25 October 2021: Database Analysis
RNA N6-Methyladenosine Patterns in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Reveal a Distinct Immune Infiltration Landscape and Clinical Significance
Hua Zhao 1CEFG , Qiujun Zhou 2BDEF , Chengwei Shi 2CD , Yaojian Shao 2CD , Junjie Ni 2CD , Jianying Lou 3ACE* , Shenyu Wei 2ACEF*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.930994
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e930994
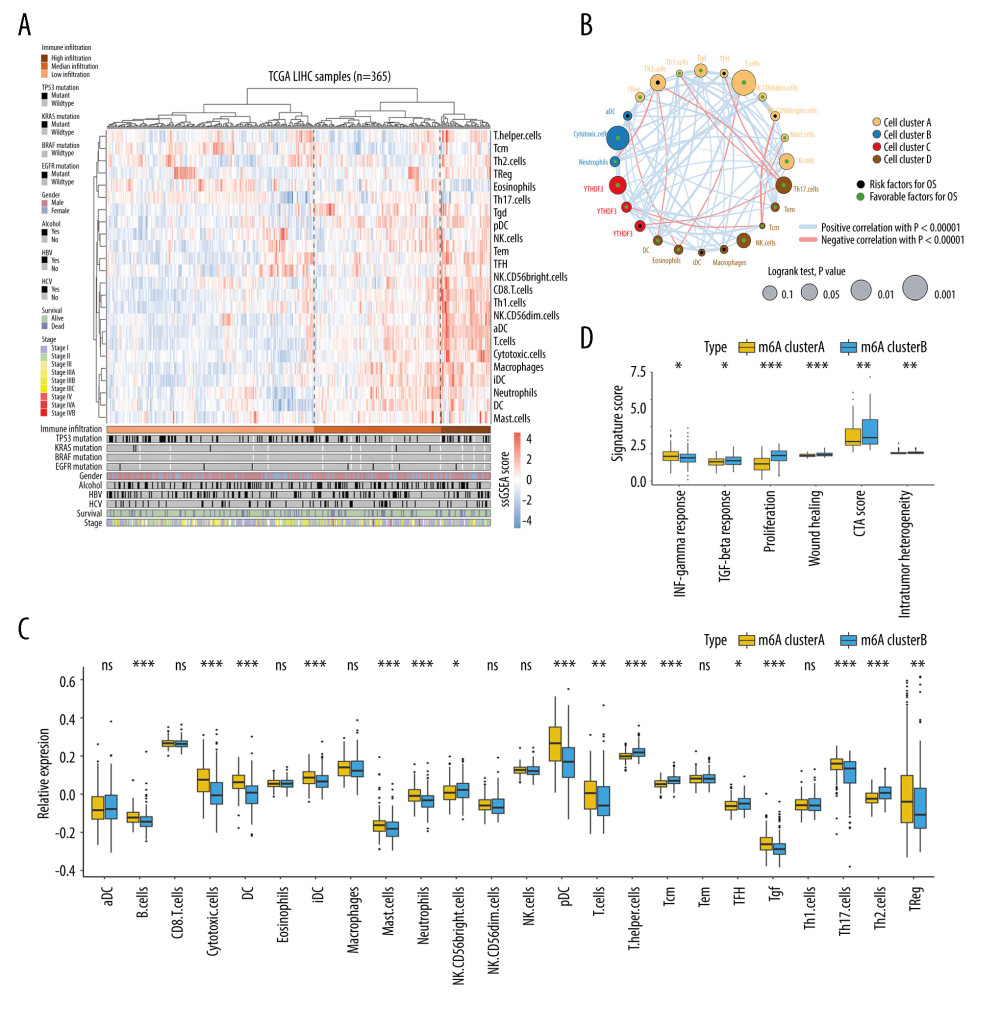
Figure 3 Immune cell infiltration characteristics in distinct N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation modification patterns. (A) Unsupervised classification of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from The Cancer Genome Atlas cohort using normalized single-sample gene set enrichment analysis scores of 24 types of immune cells. Patients were classified as having high-, median-, and low-immune infiltration status. (B) The interaction among the 24 immune cell types in the HCC tumor microenvironment. The node size was calculated by Log10(log-rank P value) and represents the impact of each immune cell type on prognosis. (C) Differences in the abundance of immune cell infiltration between the 2 m6A modification patterns. (D) Differences in IFN-gamma response, TGF-beta response, proliferation, wound healing, cancer-testis antigen score, and intratumor heterogeneity signatures between the 2 m6A modification patterns. The P value is represented by asterisks (*** P<0.001; ** P<0.01; * P<0.05). R (version 3.6.1) software was used to create the pictures.


