25 October 2021: Database Analysis
RNA N6-Methyladenosine Patterns in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Reveal a Distinct Immune Infiltration Landscape and Clinical Significance
Hua Zhao 1CEFG , Qiujun Zhou 2BDEF , Chengwei Shi 2CD , Yaojian Shao 2CD , Junjie Ni 2CD , Jianying Lou 3ACE* , Shenyu Wei 2ACEF*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.930994
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e930994
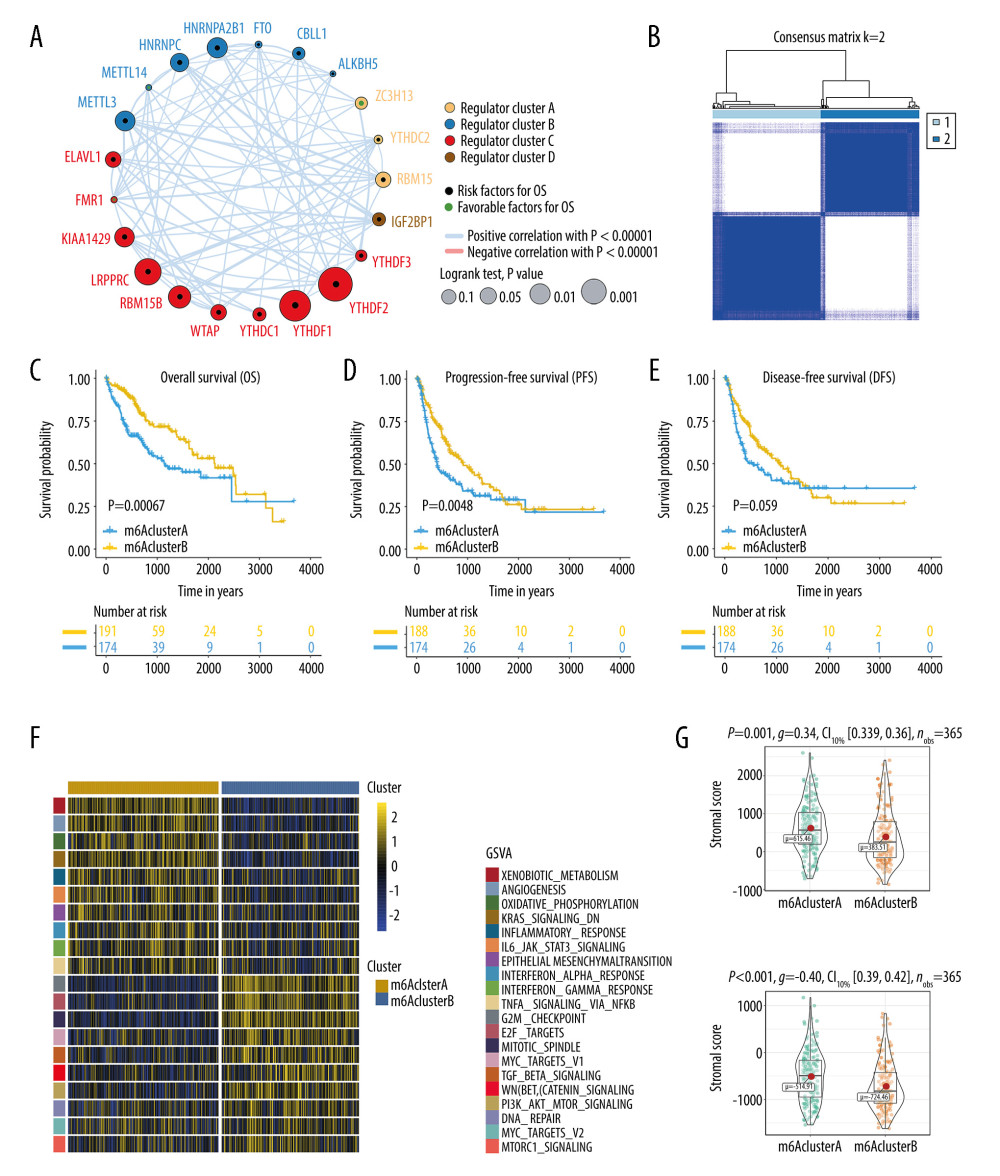
Figure 2 Survival outcomes and biological characteristics of distinct N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation modification patterns. (A) Interaction of 21 m6A methylation modulators in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The node size, measured by log10 (P value), represents the impact of each m6A modulator on prognosis. The black and green dots represent overall survival risk and protective factors, respectively. The thickness of the lines indicates the correlation strength between m6A modulators. Blue lines, positive correlation; red lines, negative correlation. (B) Consensus classification of patients with HCC for k=2. (C–E) Kaplan-Meier survival analyses for distinct m6A modification patterns in The Cancer Genome Atlas cohort. The m6A cluster B presents worse (C) overall survival, (D) progression-free survival, and (E) disease-free survival than the m6A cluster A. (F) Gene set variation analysis enrichment illustrates the activation score of biological function between 2 methylation patterns and is visualized in the heatmap. The activated pathway is marked with gold and the inhibited pathway is marked with blue. (G) Immune and stromal component differences between 2 methylation patterns. R (version 3.6.1) software was used to create the pictures.


