05 June 2021: Animal Study
Anti-Psoriatic Effects of Middle Fragment of Chlamydial Plasmid-Encoded Protein pGP3 in an Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis Mouse Model
Yiming Zhang 1A* , Miaomiao Ma 2A* , Jun Li 3D , Yingye Wu 2C , Lu Xue 2C , Rongrong Zhao 2B , Lu Wang 2E , Shuping Hou 2G* , Huiping Wang 2G*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.929781
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e929781
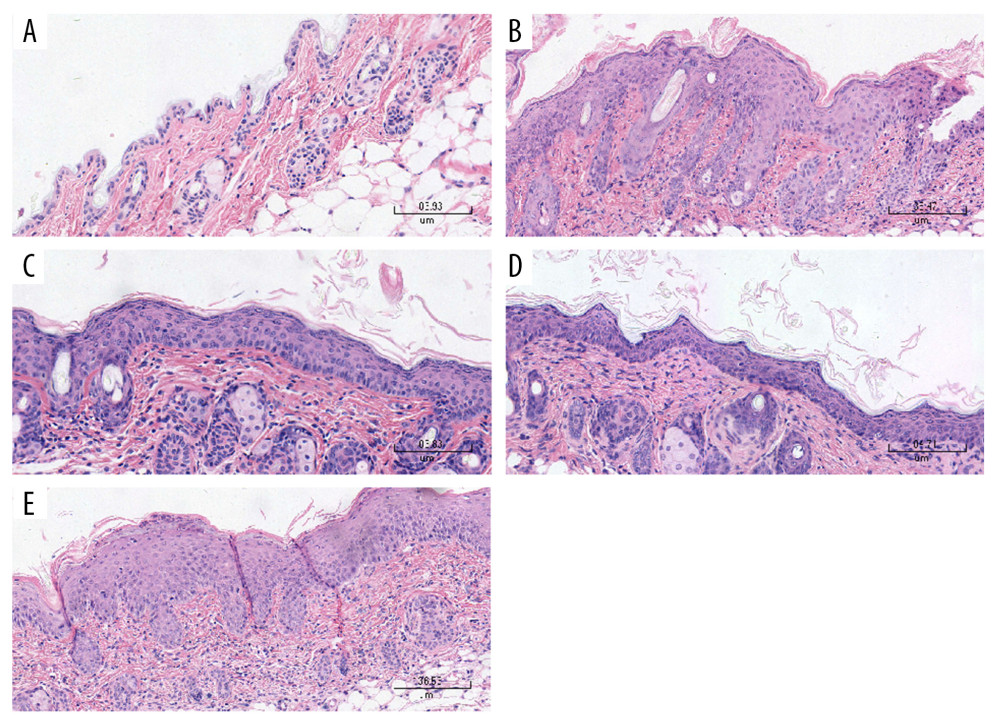
Figure 5 Histological examinations of the skin sections stained with hematoxylin-eosin (Magnification: 200×). (A) Normal mice. (B) The skin sections of the imiquimod (IMQ) group exhibited epidermal thickening, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and inflammation in the dermis. (C, D) The hyperkeratosis and acanthosis in the pGP3 (IM-pGP3) and pGP3M (IM-pGP3M) intramuscular injection groups were milder than that in the IMQ group and (E) the phosphate-buffered saline intramuscular injection group.


