14 April 2021: Animal Study
Zi Qi Decoction Alleviates Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)-Related Nuclear Factor kappa b (NF-κB) and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Signaling Pathways
Jingwen Zhou 1ABCE* , Xiaolong Zhang 1A* , Lingfeng Wan 1AD , Jun Yu 2BCD , Tianci Li 2BCD , Ziyu Lu 3BCD , Nanyuan Fang 1E , Lixia Sun 1AG* , Fang Ye 2AG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.929438
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e929438
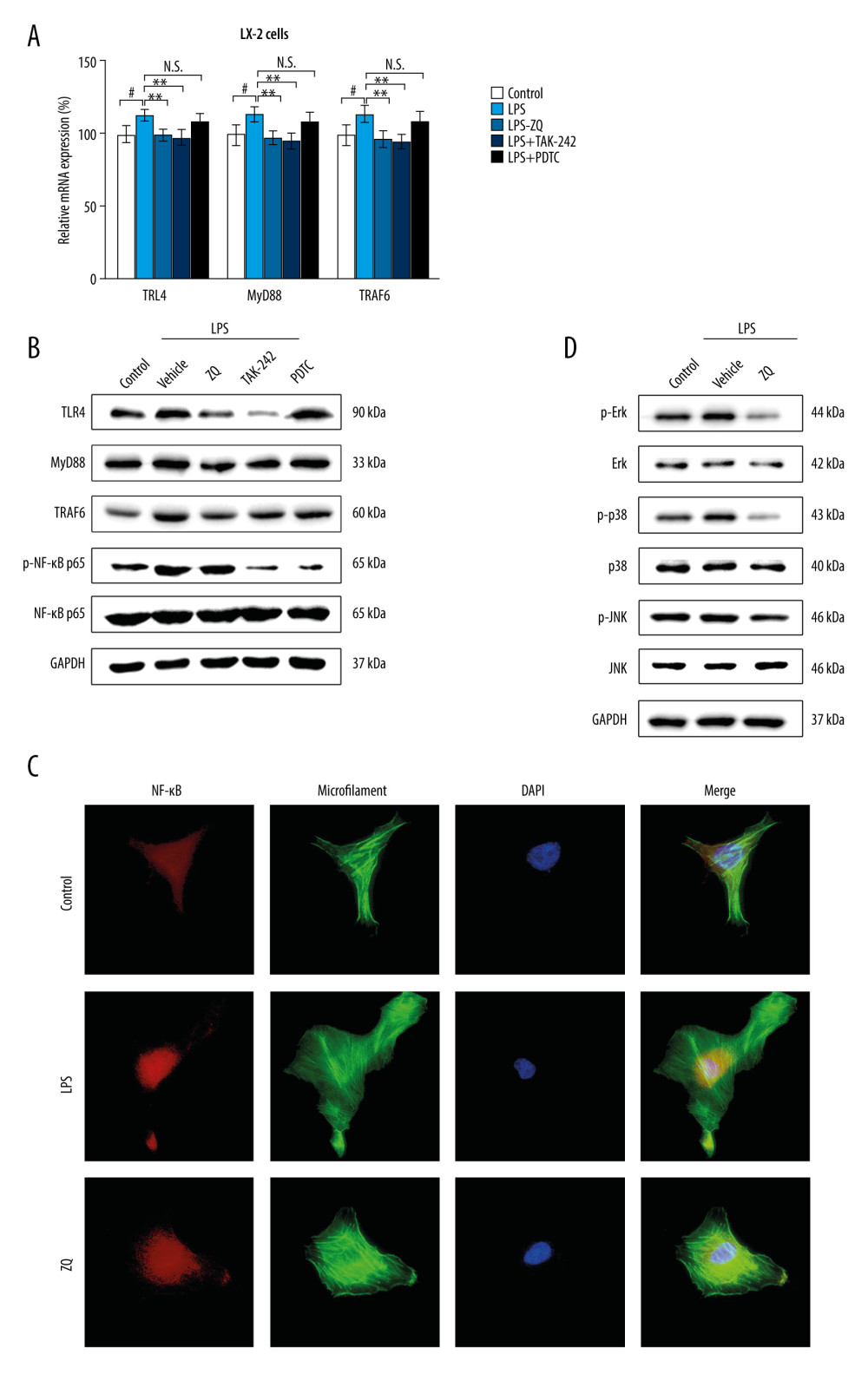
Figure 2 Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-related nuclear factor kappa b (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways were inhibited by Zi Qi decoction in vitro. (A) The effects of Zi Qi decoction on the relative messenger RNA level of cellular TLR4, MyD88, and TRAF6 in each group. (B) The effects of Zi Qi decoction on the protein level of cellular TLR4, MyD88, TRAF6, and phospho-NF-κB p65 in each group. (C) Zi Qi decoction significantly suppressed the nuclear transportation of activated NF-κB p65 in LPS-induced LX-2 cells, as determined by immunofluorescence (n=3). Magnification ×40. (D) The protein expressions of ERK, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, and p38 and their relative phosphorylation levels in each group. # P<0.05, compared with the control group. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, compared with the LPS group. Data were presented as means±standard deviations.


