26 March 2021: Animal Study
Salvianic Acid A Regulates High-Glucose-Treated Endothelial Progenitor Cell Dysfunction via the AKT/Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) Pathway
Yanhua Guan 12ABCDEF , Xu Wang 13ABCDEF*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.928153
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e928153
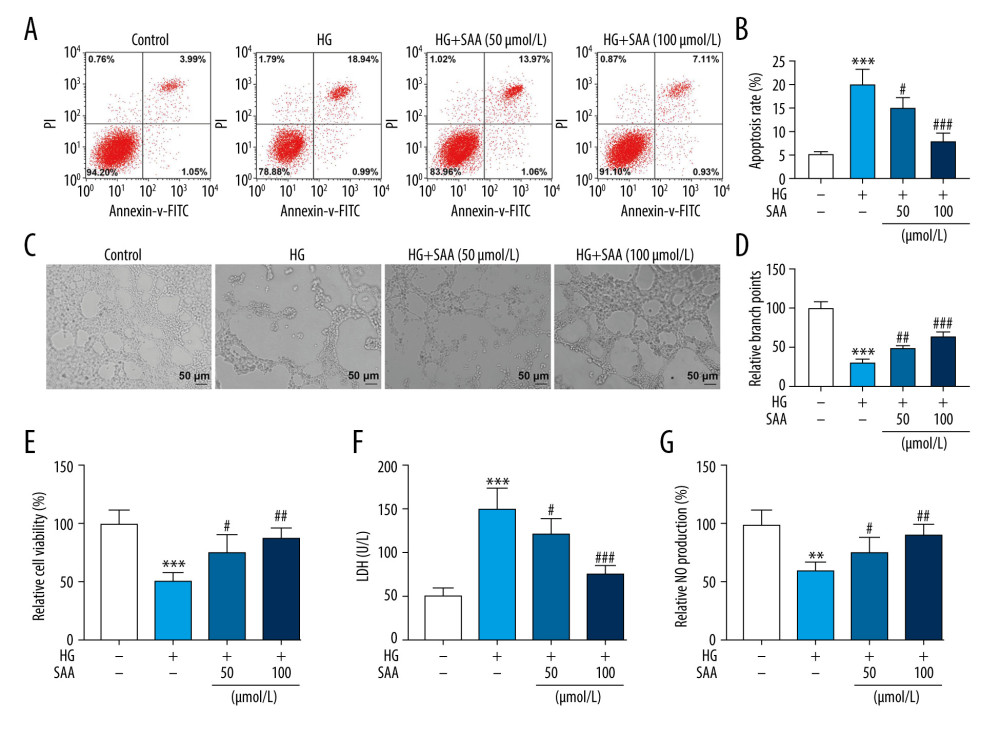
Figure 2 Salvianic acid A (SAA) at different concentrations regulated apoptosis, tube formation, viability, lactated dehydrogenase (LDH) and nitric oxide (NO) production in endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) under high concentration of glucose. (A, B) Flow cytometry showing the effect of SAA on the apoptosis of high-glucose (HG)-treated endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). *** P<0.001 compared to the control group. # P<0.05 compared to the HG group. (C, D) Tube formation assay showing the effect of SAA on the tube formation of HG-treated EPCs. *** P<0.001 compared to the control group. ## P<0.01 compared to the HG group. (E) 3-[4,5-Dimethylthylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay showing the effect of SAA on the viability of HG-treated EPCs. *** P<0.001 compared to the control group. # P<0.05 compared to the HG group. (F) LDH assay showing the effect of SAA on the cytotoxicity of HG-treated EPCs. *** P<0.001 compared to the control group. # P<0.05 compared to the HG group. (G) 3-Amino,4-aminomethyl-2′,7′-difluorescein diacetate (DAF-FM DA) was used to detect the effect of SAA on NO production in HG-treated EPCs. ** P<0.01 compared to the control group. # P<0.05 compared to the HG group. The cells were divided into 4 groups: control group (5.5 mmol/L glucose and 25 mmol/L mannitol), HG group (30 mmol/L glucose), HG+50 group (cells were pretreated with 50 μmol/L SAA for 24 h and then cultured with 30 mmol/L glucose for 24 h) and HG+100 group (cells were pretreated with 100 μmol/L SAA for 24 h and then cultured with 30 mmol/L glucose for 24 h).


