07 July 2020: Animal Study
Baicalin Suppresses Bilirubin-Induced Apoptosis and Inflammation by Regulating p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPK) Signaling in Neonatal Neurons
Shuang Shi 1ABCDEF* , Qianwei Cui 1ACE* , Jing Xu 1CDEF , Zhiguo Tang 1ABC , Binya Shi 2ABCDEF* , Zhongwei Liu 1ABCDEFG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.926441
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e926441
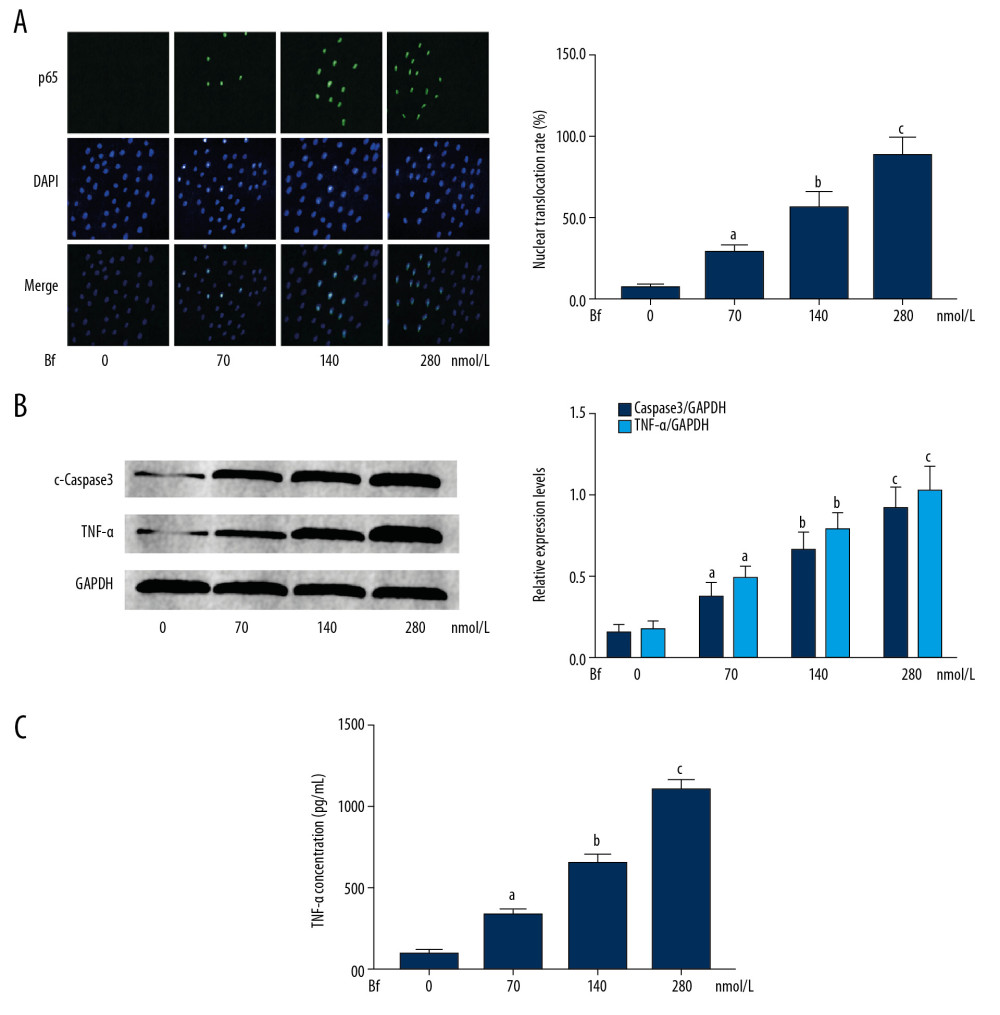
Figure 3 (A) Immunofluorescent staining was used to evaluate the nuclear translocation of p65. p65 was tagged with green fluorescence (Alexa488) and nuclei were tagged with blue fluorescence (DAPI). Columns indicate the relative nuclear translocation rate of p65 in neurons incubated with Bf at concentrations of 0, 70, 140, and 280 nmol/L. (B) Western blotting was used to determine the relative expression levels of proteins. Immunoblots of cleaved caspase3 (c-caspase3), TNF-α, and GAPDH (internal reference) of neurons. Columns indicate the relative expression levels of c-caspase3 and TNF-α in neurons incubated with Bf at concentrations of 0, 70, 140, and 280 nmol/L. (C) ELISA was used to detect concentration of cytokines. Columns indicate the concentrations of TNF-α in cell medium of neurons incubated with Bf at concentrations of 0, 70, 140, and 280 nmol/L. [n=10; a difference was significant when compared with neurons incubated with control; b difference was significant when compared with neurons incubated with Bf at 70 nmol/L; c difference was significant when compared with neurons incubated with Bf at 140 nmol/L].


