23 November 2020: Clinical Research
Altered Brain Network Centrality in Patients with Adult Strabismus with Amblyopia: A Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Study
Kang-Rui Wu 1ABCD* , Ya-Jie Yu 1ABCD* , Li-Ying Tang 2BCDE* , Si-Yi Chen 1BCDF , Meng-Yao Zhang 1ABCD , Tie Sun 1ABCF , Shi-Nan Wu 1ABCF , Kang Yu 1BCDF , Biao Li 1BCF , Yi Shao 1ABCDEF*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.925856
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e925856
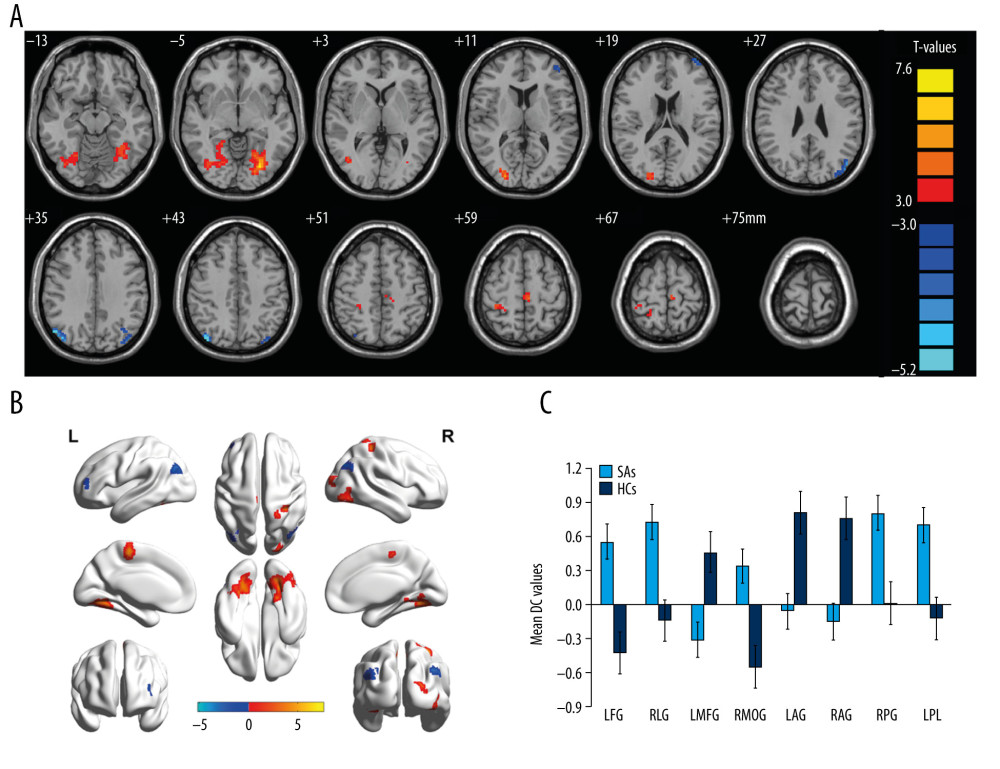
Figure 2 Comparison of DC in adult strabismus with amblyopia patients and HC groups. (A, B) Notable differences in DC of the brain were observed. Significant differences in DC were observed in the left fusiform gyrus, right lingual gyrus, left middle frontal gyrus, right middle occipital gyrus, left angular gyrus, angular gyrus, right postcentral gyrus, and left paracentral lobule. The red area represents higher DC value, while the blue area represents lower DC value. Multiple comparison using gaussian random field (GRF) theory (Z >2.3, column by column P<0.05). (C) The mean DC values of the brain between the adult strabismus with amblyopia patients and HC groups. DC – degree center; SAs – strabismus with amblyopia; HCs – healthy control groups; LFG – left fusiform gyrus; RLG – right lingual gyrus; LMFG – left middle frontal gyrus; RMOG – right middle occipital gyrus; LAG – left angular gyrus; RAG – angular gyrus; RPG – right postcentral gyrus; LPL – left paracentral lobule; R – right; L – left.


