29 June 2020: Animal Study
Kupffer Cells Regulate Natural Killer Cells Via the NK group 2, Member D (NKG2D)/Retinoic Acid Early Inducible-1 (RAE-1) Interaction and Cytokines in a Primary Biliary Cholangitis Mouse Model
Hai-Yan Fu 1EF , Wei-Min Bao 2C , Cai-Xia Yang 1D , Wei-Ju Lai 1D , Jia-Min Xu 1B , Hai-Yan Yu 1B , Yi-Na Yang 1B , Xu Tan 1B , Ajay Kumar Gupta 1F , Ying-Mei Tang 1AG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.923726
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e923726
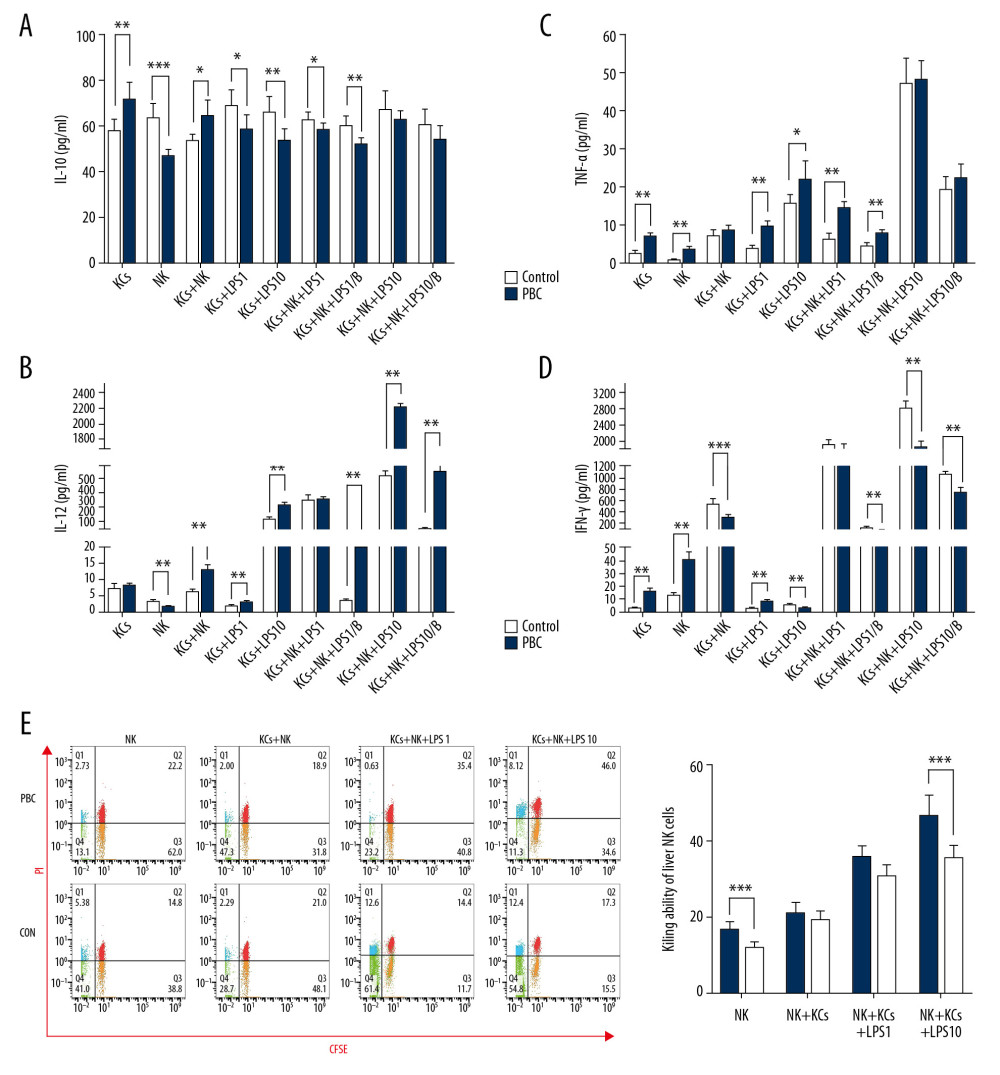
Figure 4 The expression of cytokines in each group of cultured cells and the NK cell-killing ability. (A) The expression of IL-10 in each culture system is expressed as the mean±SEM, and the experiment was repeated 3 times; *** P<0.001, * P<0.05, ** P<0.01. (B) Expression of IL-12 in each culture system. Data are expressed as the mean±SEM, and the experiment was repeated three times; ** P<0.01. (C) Expression of TNF-α in each culture system. Data are expressed as the mean±SEM, and the experiment was repeated 3 times; ** P<0.01. (D) Expression of IFN-γ in each culture system. Data are expressed as the mean±SEM, and the experiment was repeated 3 times; *** P<0.001, ** P<0.01. (E) YAC-1 cell-killing ability of NK cells isolated from liver tissue from mice in the PBC and CON groups. The experiment was repeated 3 times, and a histogram shows statistically significant differences; *** P<0.001. NK – natural killer; IL – interleukin; SEM – standard error of the mean; TNF – tumor necrosis factor; IFN-γ – interferon-γ.


