29 June 2020: Animal Study
Kupffer Cells Regulate Natural Killer Cells Via the NK group 2, Member D (NKG2D)/Retinoic Acid Early Inducible-1 (RAE-1) Interaction and Cytokines in a Primary Biliary Cholangitis Mouse Model
Hai-Yan Fu 1EF , Wei-Min Bao 2C , Cai-Xia Yang 1D , Wei-Ju Lai 1D , Jia-Min Xu 1B , Hai-Yan Yu 1B , Yi-Na Yang 1B , Xu Tan 1B , Ajay Kumar Gupta 1F , Ying-Mei Tang 1AG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.923726
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e923726
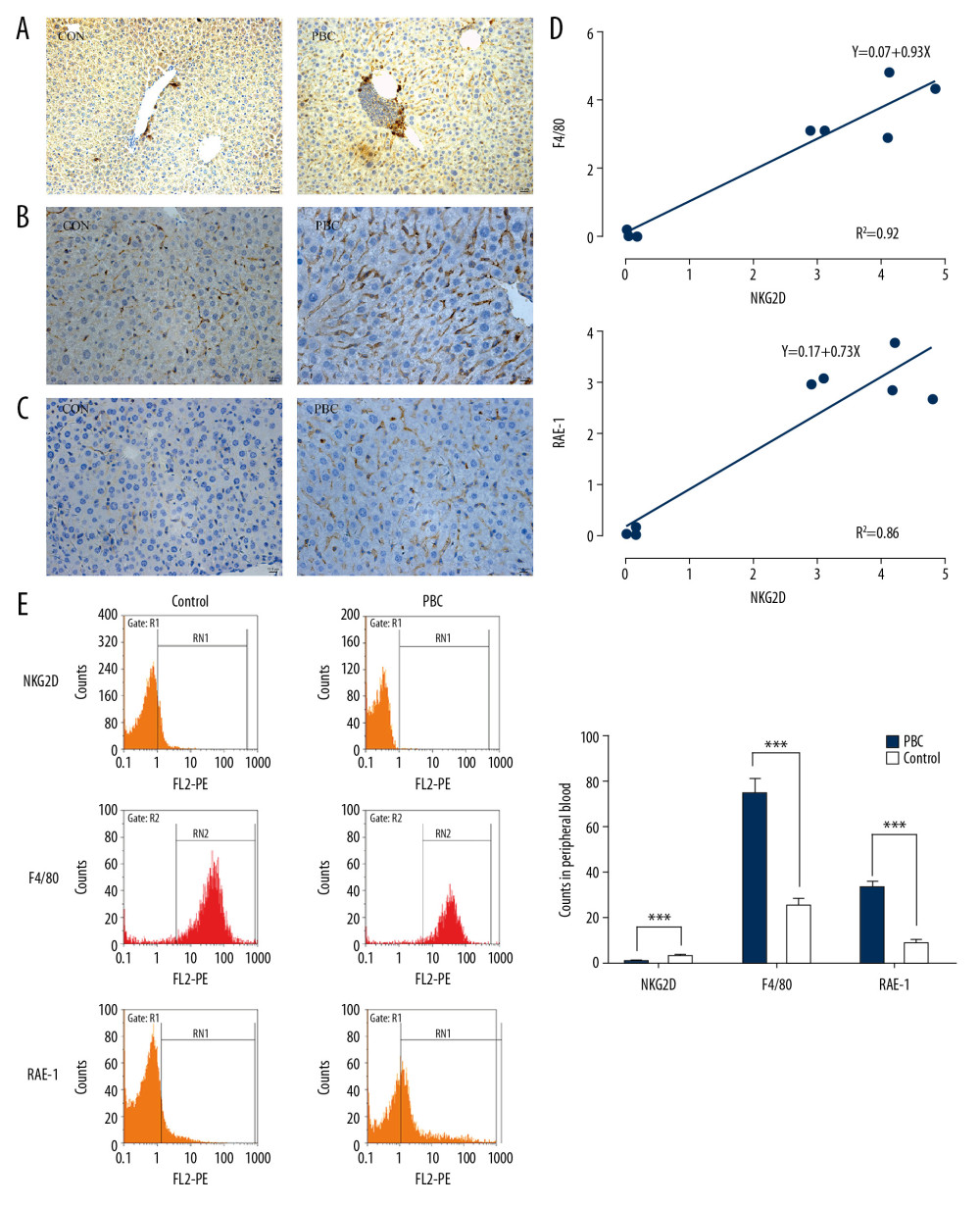
Figure 2 Expression of NKG2D and its ligand in the livers and peripheral blood of mice. (A) Expression of NKG2D in the livers of mice in the PBC and CON groups at 8 weeks was determined by immunohistochemistry. (B) Expression of F4/80 in the livers of mice in the PBC and CON groups at 8 weeks was determined by immunohistochemistry. (C) Expression of RAE-1 in the livers of mice in the PBC and CON groups at 8 weeks was determined by immunohistochemistry. (D) Correlation curves for NKG2D and F4/80 expression and NKG2D and RAE-1 expression in the peripheral blood from PBC mice; r=−0.754 and r=−0.866, respectively, n=6. (E) Flow cytometry showing the expression of NKG2D, F4/80 and RAE-1 in the peripheral blood of mice in the PBC and CON groups. Data are expressed as a count; n=5 for each group. Specific data are displayed as a histogram, *** P<0.001. NKG2D – natural killer group 2, member D; PBC – primary biliary cholangitis; CON – control; RAE-1 – retinoic acid early inducible-1.


