16 August 2020: Animal Study
Extract EGb761 Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Experimental Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice by Regulating the Balance of M1/M2 Macrophages and Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB)-Mediated Cellular Apoptosis
Ling Pan AD* , Yuehong Lu BCE , Zhanhua Li BCEF , Yuping Tan BF , Hongmei Yang BF , Ping Ruan CDF , Ruixiang Li BFDOI: 10.12659/MSM.922634
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e922634
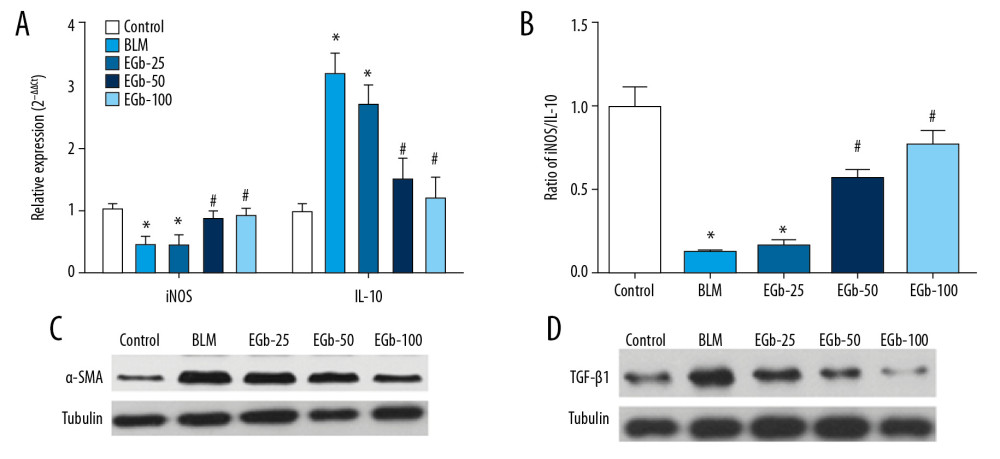
Figure 4 EGb761 regulates the balance of M1/M2 macrophages and expression of inflammation-associated proteins to prevent pulmonary fibrosis (PF). (A) Messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) expression levels of M1 (inducible nitric oxide synthase [iNOS]) and M2 (interleukin [IL]-10) macrophage markers in PF lung tissues were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and tubulin served as a reference control and a loading control, respectively. (B) Ratio of M1 and M2 macrophages in lung tissues was calculated on the basis of the mRNA expression of iNOS and IL-10. The expression level of α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) (C) and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 (D) in lung tissues was determined on day 28 after treating with BLM or EGb761 by western blotting. * P<0.05 vs. normal group; # P<0.05 vs. BLM group.


