15 June 2020: Clinical Research
LncRNA LINC00152 Increases the Aggressiveness of Human Retinoblastoma and Enhances Carboplatin and Adriamycin Resistance by Regulating MiR-613/Yes-Associated Protein 1 (YAP1) Axis
Ying Wang CDE* , Danli Xin ABCE , Lei Zhou BCDFDOI: 10.12659/MSM.920886
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e920886
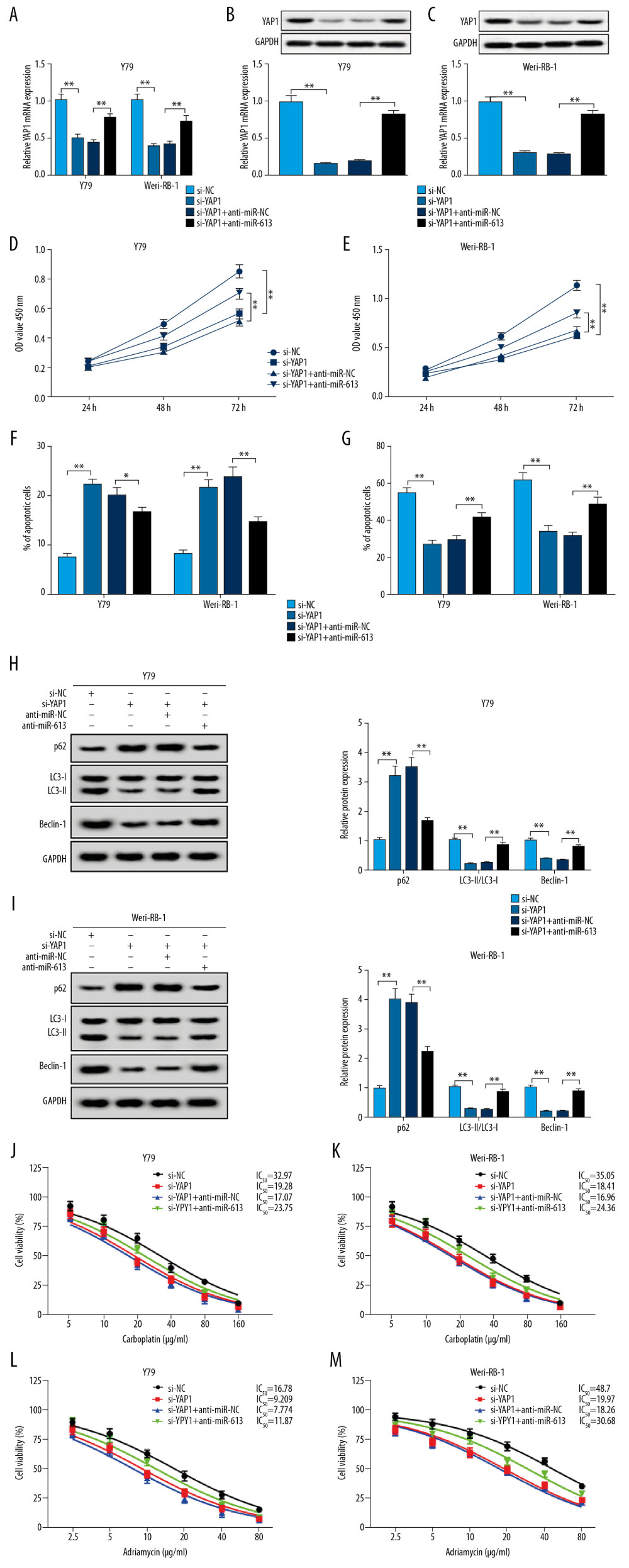
Figure 6 MiR-613 regulated proliferation, invasion, autophagy, apoptosis and chemoresistance of retinoblastoma cells by affecting YAP1 expression. (A–M) Y79 and Weri-RB-1 cells were transfected with si-NC, si-YAP1, si-YAP1+anti-miR-NC, or si-YAP1+anti-miR-613. (A–C) The expression levels of YAP1 in transfected Y79 and Weri-RB-1 cells were measured by RT-qPCR and western blot assays. (D, E) Cell viability was evaluated by CCK-8 assay in Y79 and Weri-RB-1 cells after transfection. (F) Cell apoptosis rate was analyzed in Y79 and Weri-RB-1 cells with flow cytometry assay. (G) Transwell assay was performed to assess invasion ability of Y79 and Weri-RB-1 cells post-transfection. (H, I) The protein expression levels of p62, LC3-I, LC3-II and Beclin-1 were determined with western blot assay. (J–M) IC50 value of carboplatin and adriamycin in Y79 and Weri-RB-1 cells was calculated with CCK-8 assay. ** P<0.01. RT-qPCR – real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; CCK-8 – Cell Counting Kit-8.


